Exam Code: BCABA
Exam Name: Board Certified Assistant Behavior Analyst
Certification Provider: BACB
Corresponding Certification: BCaBA
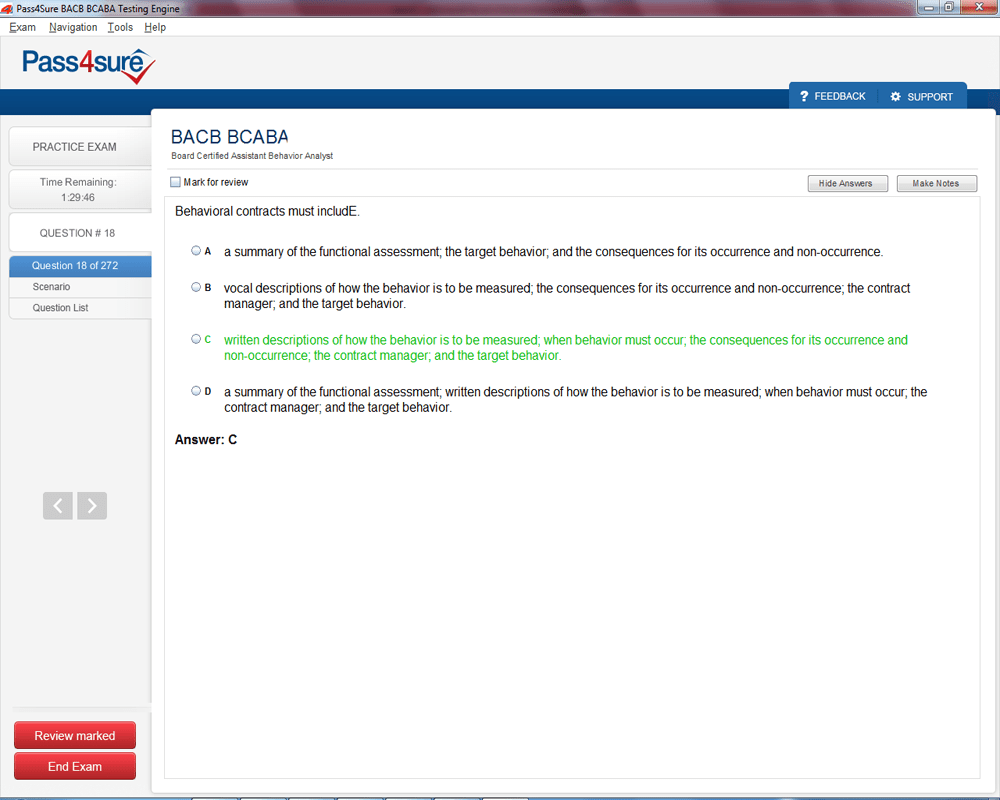
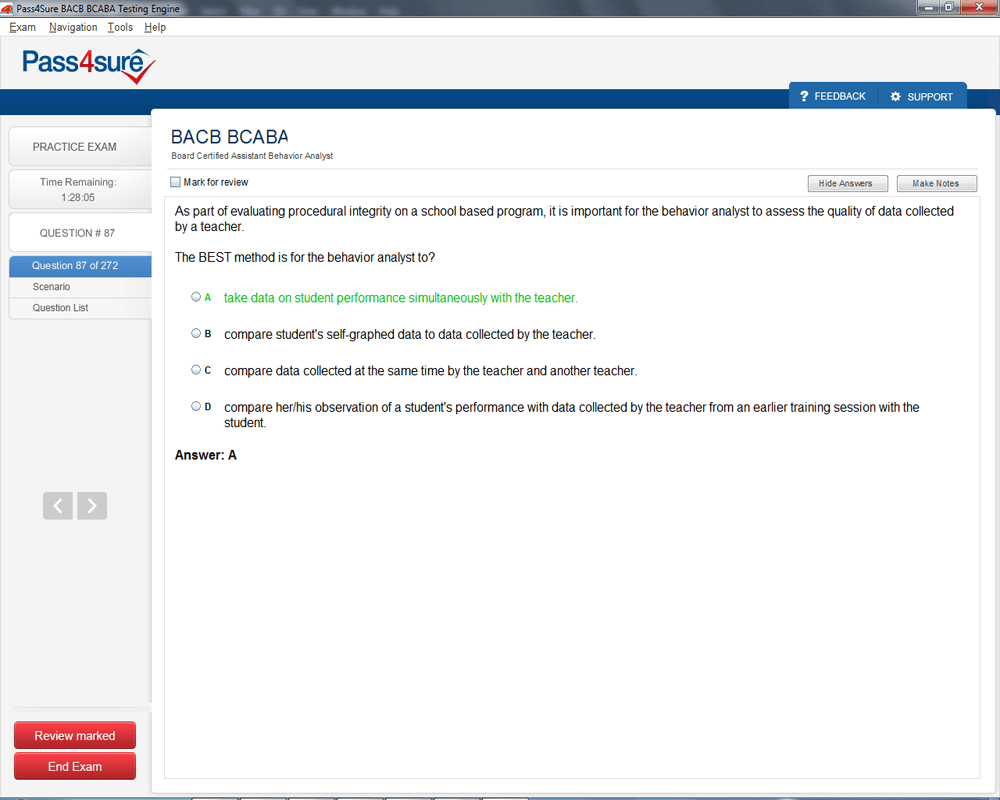
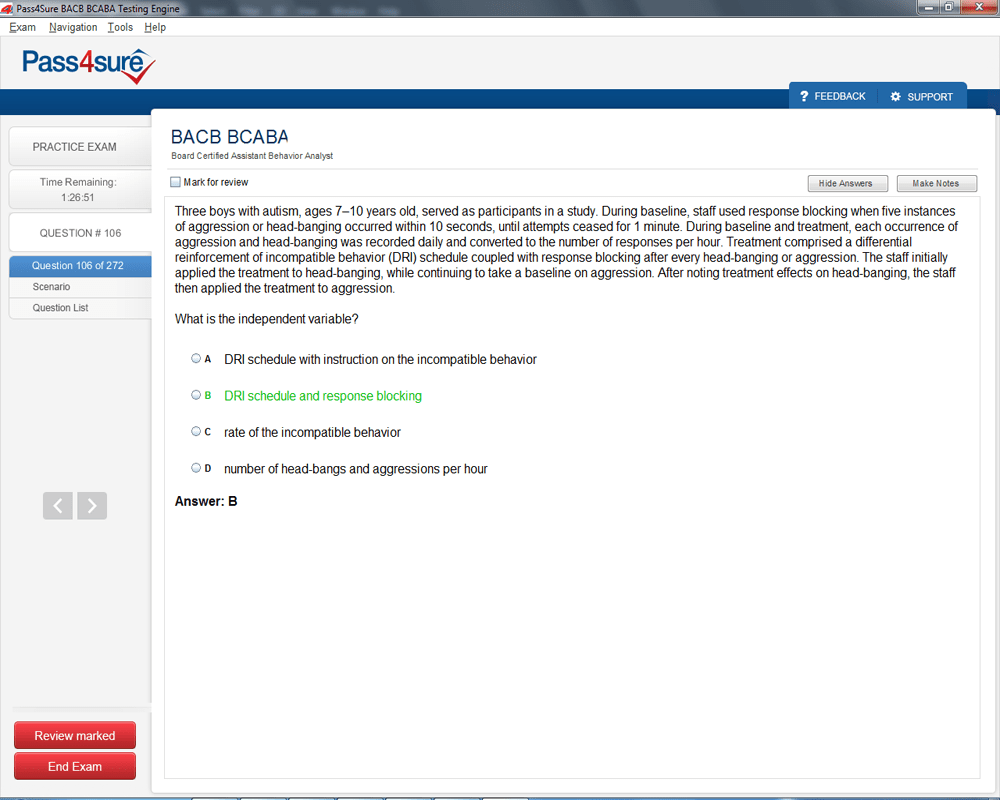
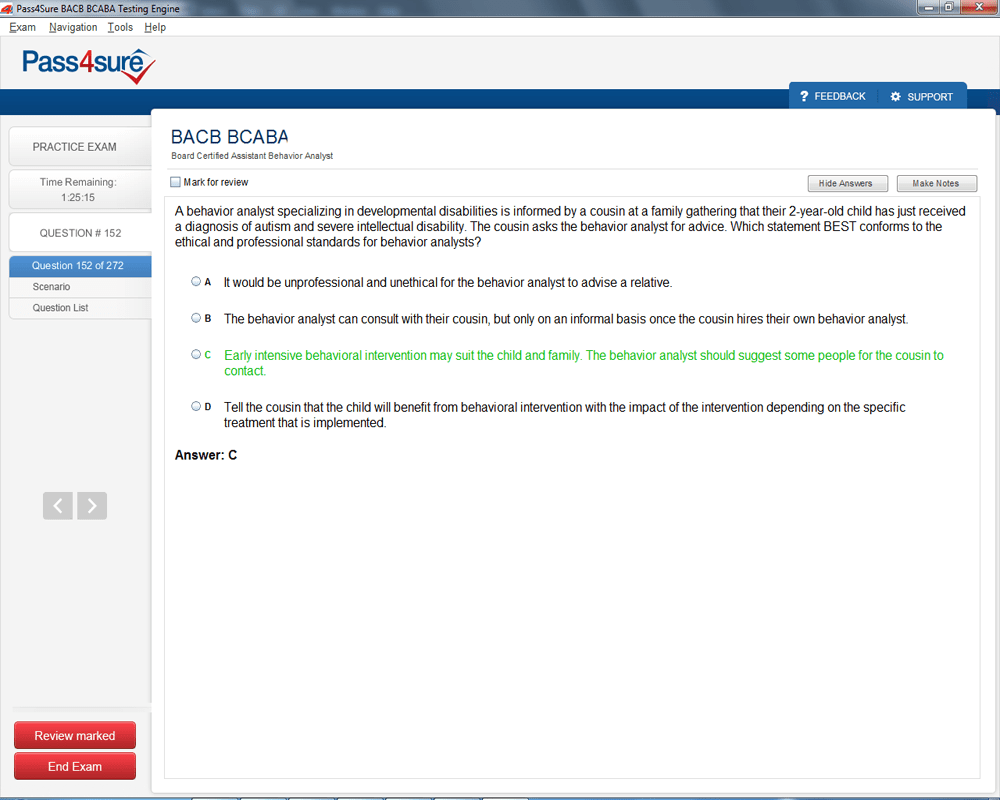
BCABA Exam Product Screenshots
Frequently Asked Questions
How does your testing engine works?
Once download and installed on your PC, you can practise test questions, review your questions & answers using two different options 'practice exam' and 'virtual exam'. Virtual Exam - test yourself with exam questions with a time limit, as if you are taking exams in the Prometric or VUE testing centre. Practice exam - review exam questions one by one, see correct answers and explanations.
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Pass4sure products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Pass4sure software on?
You can download the Pass4sure products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email sales@pass4sure.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What are the system requirements?
Minimum System Requirements:
- Windows XP or newer operating system
- Java Version 8 or newer
- 1+ GHz processor
- 1 GB Ram
- 50 MB available hard disk typically (products may vary)
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
BCABA Complete Prep: Key Concepts and Insider Tips
Embarking on the path toward Board Certified Assistant Behavior Analyst (BCABA) certification necessitates a deliberate orchestration of study and practice. The journey begins with constructing a structured framework that anchors understanding in fundamental behavioral principles. Without a coherent foundation, the vast terrain of applied behavior analysis can feel labyrinthine, with theoretical concepts blending into abstract notions that lack immediate clarity. Segmenting preparation into thematic layers allows for incremental mastery, ensuring that each building block reinforces the next. For instance, immersing oneself initially in the principles of reinforcement—both positive and negative—serves as a cornerstone for appreciating subsequent strategies such as extinction, punishment, and stimulus control. By cultivating a methodical progression, learners transform overwhelming content into a navigable architecture of knowledge, where each segment has practical applicability.
Visual mapping of behavioral contingencies adds another dimension to structured learning. Flowcharts depicting antecedent-behavior-consequence relationships, diagrams illustrating reinforcement schedules, and schematics of skill acquisition programs crystallize abstract notions into observable patterns. The brain is innately responsive to visual representation, and integrating diagrams with textual study reinforces retention while facilitating rapid cognitive retrieval. Moreover, repeated interaction with visual frameworks nurtures analytical agility, enabling practitioners to swiftly interpret complex scenarios in both exam and real-world contexts. Over time, these strategies converge into a disciplined cognitive scaffold, fostering confidence in both comprehension and application.
Mastering Terminology Through Applied Context
Fluency in the specialized language of behavior analysis is a crucial determinant of both exam performance and clinical efficacy. Terms such as discriminative stimulus, shaping, response cost, and functional assessment are not mere lexical constructs; they encapsulate operational strategies that guide intervention planning. The challenge lies not only in memorization but in embedding these terms within a functional understanding that allows rapid recognition and execution in practical contexts. One effective method is contextual immersion, wherein each concept is practiced within hypothetical or simulated case scenarios. Role-playing exercises, for instance, enable learners to navigate the interplay between antecedents, behaviors, and consequences, thereby transforming abstract definitions into actionable insight.
Consider a scenario where a child exhibits aggression when presented with an academic task. A practitioner adept in behavioral terminology and conceptual application can identify the triggering antecedent, evaluate the function of the behavior, and implement targeted interventions. The ability to articulate and operationalize such terms ensures that strategies are not theoretical abstractions but actionable tools capable of influencing meaningful behavioral change. Repetition and applied practice refine both comprehension and confidence, bridging the gap between intellectual understanding and real-world effectiveness.
Precision in Data Collection and Interpretation
Data collection constitutes a cornerstone of BCABA proficiency. Beyond knowing interventions, a competent practitioner must measure outcomes with precision and interpret trends with analytic discernment. Various methodologies exist for capturing behavioral data, including frequency counts, duration recording, interval recording, and latency measurement. Selecting the appropriate tool for a given scenario requires an understanding of both behavioral characteristics and measurement nuances. For example, measuring the frequency of discrete skill responses is well-suited for skill acquisition programs, whereas duration recording illuminates the intensity and persistence of disruptive behaviors.
Interpretation of data extends beyond numeric tabulation. Patterns often emerge subtly, requiring practitioners to detect trends, anomalies, and interactions between interventions and environmental variables. Skillful analysis informs iterative adjustments, ensuring interventions remain dynamic rather than static. The ability to translate raw data into actionable insight distinguishes proficient practitioners from those who rely solely on theoretical knowledge. Over time, this analytical capacity evolves into a habitual cognitive process, where observation, measurement, and interpretation coalesce seamlessly, preparing candidates for both exam scenarios and complex clinical decision-making.
Navigating Ethical Frameworks in Applied Practice
Ethics in applied behavior analysis embodies more than adherence to a code; it represents an active, ongoing negotiation between professional responsibility and real-world exigencies. The BCABA exam rigorously evaluates this dimension, presenting scenarios where ethical reasoning must guide decisions in contexts of ambiguity and competing priorities. Concepts such as beneficence, nonmaleficence, fidelity, and professional responsibility serve as guiding principles that transcend prescriptive rules, requiring nuanced interpretation and conscientious application.
Practical engagement with ethics can be enhanced through case-based exploration, wherein learners examine dilemmas such as client autonomy versus organizational constraints, or the tension between accurate data collection and external pressures to alter outcomes. Reflective practice, discussion groups, and situational analysis cultivate a depth of understanding that theoretical study alone cannot achieve. Ethical acuity is honed through deliberate consideration, repeated exposure to diverse scenarios, and introspective evaluation of decision-making processes. This integration of reflection, application, and professional judgment ensures that ethical reasoning becomes an intuitive component of both examination performance and daily practice.
Strategic Time Management and Cognitive Endurance
The temporal dimension of preparation and examination is frequently underestimated, yet it is pivotal to success. The BCABA exam requires sustained cognitive engagement, where prolonged attention and analytical precision are essential. Fatigue, even subtle, can erode memory retrieval, compromise problem-solving, and magnify the likelihood of errors. Structured study schedules that balance intensive review with periods of rest optimize both retention and mental endurance, allowing cognitive systems to consolidate learning effectively.
During examination, time allocation becomes a strategic skill. Careful reading of scenarios, systematic evaluation of options, and deliberate pacing mitigate the risk of impulsive responses. Simulated practice under timed conditions fosters familiarity with cognitive demands, reducing anxiety and enhancing performance accuracy. Over time, this strategic approach to temporal management cultivates resilience, enabling candidates to navigate both the concentrated demands of exam conditions and the continuous attentional requirements of clinical practice.
Cultivating Active Engagement in Learning
Active engagement represents a transformative approach to mastery, shifting the learner from passive absorption to dynamic participation. Teaching concepts to peers, verbalizing reasoning, and explaining principles aloud establish neural connections that facilitate rapid retrieval and deeper comprehension. This methodology is particularly effective in applied behavior analysis, where abstract principles gain clarity through articulation and contextual application.
For instance, discussing the distinctions between continuous and intermittent reinforcement allows the learner to synthesize definitions, operational mechanics, and practical implications simultaneously. Such engagement fosters analytical depth, exposing subtleties and interactions that might remain obscure through solitary reading. Moreover, active learning encourages iterative reflection, where comprehension is continuously evaluated and reinforced, creating a self-sustaining cycle of cognitive development. Over time, these practices engender a robust, flexible understanding that supports both exam success and professional competency.
Integrating Knowledge Into Practical Expertise
The culmination of BCABA preparation resides in the seamless integration of knowledge, skills, and judgment into functional expertise. Mastery of behavioral principles, fluency in terminology, precision in data collection, ethical reasoning, strategic time management, and active engagement coalesce into a holistic capability. Each component reinforces the others: ethical reasoning informs data interpretation, mastery of principles guides intervention selection, and active engagement strengthens both comprehension and application.
This integrated expertise is not merely performative but operative, influencing outcomes in real-world settings where the complexity and variability of human behavior challenge rigid application of theory. Practitioners who internalize these competencies demonstrate adaptability, reflective judgment, and procedural fluency. They navigate behavioral contingencies with discernment, anticipate outcomes with informed foresight, and adjust strategies responsively based on empirical observation. In this manner, the BCABA credential becomes not only a validation of knowledge but an embodiment of practical proficiency, where preparation and experience converge to yield meaningful, measurable impact.
Foundations of Behavioral Assessment in BCABA Practice
Behavioral assessment serves as the cornerstone of effective intervention in applied behavior analysis. Understanding the nuances of human behavior demands more than casual observation; it requires a meticulous approach to data collection, interpretation, and functional understanding. Practitioners must discern subtle patterns that reveal why behaviors occur, how they persist, and what conditions influence their intensity. Within BCABA preparation, cultivating this analytical mindset is crucial, as it underpins the ability to make informed, ethical decisions in real-world practice. The assessment process is not a singular act but a multifaceted endeavor, combining observational rigor with structured methodologies. Each stage of assessment provides insights that guide intervention design, ensuring that strategies are not arbitrary but precisely tailored to individual needs.
The framework for behavioral assessment emphasizes systematic evaluation, with the goal of identifying antecedents, behaviors, and consequences that interact to produce observable outcomes. Candidates are expected to recognize the significance of environmental context, task demands, and social dynamics in shaping behavior. High-quality assessment integrates multiple sources of information, ranging from caregiver interviews to historical records, forming a comprehensive profile of the individual. By mastering these principles, BCABA candidates enhance their ability to anticipate behavioral patterns and implement interventions that are both effective and ethically sound.
Functional Behavior Assessment: A Strategic Approach
Functional behavior assessment represents a methodical approach to uncovering the underlying purpose of behavior. Rather than treating behavior as a random occurrence, FBA provides a structured pathway to understanding its function. The process involves identifying the antecedents that precede behavior, the behavior itself, and the consequences that maintain it. Patterns emerge through careful observation, revealing whether behaviors are reinforced by attention, avoidance, tangible items, or sensory experiences. Recognizing these functions allows practitioners to design interventions that address the root cause rather than merely suppressing symptoms.
A critical component of FBA is its reliance on multiple assessment methods. Direct observation provides objective data on how behaviors manifest across different settings, whereas indirect methods, such as interviews and questionnaires, capture contextual and historical information that may not be immediately observable. The integration of these data sources enriches the understanding of the individual’s behavioral repertoire, offering a robust foundation for intervention planning. Functional behavior assessment also emphasizes the need for consistency and reliability in data collection, ensuring that conclusions drawn from observations are both valid and replicable.
Direct and Indirect Assessment Methods
Assessment strategies within BCABA practice are divided into direct and indirect approaches, each offering distinct insights. Direct observation involves real-time monitoring of behavior within naturalistic or structured environments. This method allows practitioners to record frequency, duration, intensity, and context, producing tangible data that reflect the individual’s actual performance. For example, documenting the occurrence of aggressive behaviors during structured learning tasks can clarify the influence of environmental demands on behavior.
Indirect assessment complements direct observation by gathering subjective reports from caregivers, teachers, or other relevant stakeholders. These methods include interviews, rating scales, and questionnaires, which offer valuable context regarding the individual’s history, environmental triggers, and social dynamics. Although indirect methods lack the objectivity of direct observation, they provide critical information that helps generate hypotheses for functional analysis. Effective assessment integrates both approaches, combining the precision of direct measurement with the richness of contextual insight to create a multidimensional understanding of behavior.
Functional Analysis: Testing Hypotheses About Behavior
Functional analysis extends the principles of FBA by actively testing hypotheses regarding the function of behavior. This process involves manipulating antecedents and consequences to observe changes in behavior, providing empirical evidence for its underlying purpose. Functions typically include attention-seeking, escape, access to tangible items, or sensory reinforcement. Identifying the correct function is essential, as interventions must target the reinforcing mechanism to achieve meaningful behavior change.
For instance, a behavior maintained by attention may respond to interventions that provide appropriate social reinforcement while minimizing inadvertent reinforcement of problematic behavior. Conversely, sensory-maintained behaviors require strategies that satisfy sensory needs in safer or more functional ways. Functional analysis is a cornerstone of BCABA preparation, as candidates frequently encounter exam scenarios requiring interpretation of complex functional data and selection of appropriate assessment strategies. Mastery of this process ensures that interventions are not only effective but aligned with the behavioral function, enhancing overall treatment efficacy.
Data Collection and Reliability
Accurate data collection is fundamental to effective assessment and subsequent intervention. Recording behavior involves more than counting occurrences; it requires careful attention to methodological rigor, including reliability, validity, and ethical considerations. Interobserver agreement is a critical measure, ensuring that multiple observers independently record behavior consistently. High interobserver reliability reduces bias, enhances credibility, and supports confident interpretation of results.
Different recording methods are suitable for different behaviors. Event recording is ideal for discrete, countable behaviors, while interval or momentary time sampling is better suited for continuous or high-frequency behaviors. Each method requires careful selection to ensure that collected data accurately reflect the behavioral phenomenon of interest. Additionally, maintaining detailed and organized records is essential for ethical practice, allowing practitioners to document progress, evaluate intervention effectiveness, and provide transparent reports to stakeholders.
Skill Acquisition Assessment
Assessment extends beyond problem behaviors to encompass skill acquisition. Evaluating baseline performance across communication, social, and adaptive domains allows practitioners to set meaningful, measurable goals. Task analysis plays a pivotal role, breaking complex skills into manageable components. By examining each step, practitioners can provide targeted instruction and reinforcement, fostering skill mastery incrementally.
For example, teaching a self-care routine such as handwashing requires analyzing multiple discrete steps, from turning on the tap to drying hands. Observing where difficulties arise informs intervention planning, ensuring that each step is taught effectively. Skill acquisition assessment also involves continuous monitoring, adjusting goals and strategies as the individual progresses. This dynamic process ensures that interventions are individualized, responsive, and grounded in observable data rather than assumptions.
Ethical Considerations in Assessment
Ethics permeate every stage of behavioral assessment. Practitioners must ensure confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and utilize non-harmful methods. Ethical dilemmas may arise when caregivers request alterations to data, or when environmental constraints limit standard procedures. Navigating these situations requires a balance between professional standards and practical realities, emphasizing that technical competence and ethical judgment are inseparable.
BCABA candidates are expected to integrate ethical principles with practical assessment skills. This includes recognizing potential conflicts of interest, maintaining impartiality in observation and data interpretation, and prioritizing client welfare above convenience or expedience. Ethical practice is not an ancillary component but a foundational element, shaping every decision from data collection to intervention implementation. Developing this ethical awareness strengthens both professional credibility and the overall quality of behavioral services.
Practical Application of Assessment Skills
Practical experience is essential for mastering assessment skills. Candidates benefit from repeated engagement with assessment materials, such as observation forms, mock data sets, and sample case studies. Practicing the identification of antecedents, behaviors, and consequences fosters fluency, making it easier to analyze complex scenarios under exam conditions. By combining conceptual knowledge with hands-on practice, candidates cultivate the ability to translate theoretical understanding into applied skill.
Engagement with diverse cases enhances adaptability, preparing practitioners for real-world variability. Each individual presents unique patterns, contexts, and challenges, requiring flexible application of assessment principles. Through deliberate practice, candidates learn to identify subtle environmental influences, predict behavioral trends, and recommend interventions that are evidence-based, functional, and respectful of client dignity. This iterative process solidifies confidence, competence, and the ability to perform at a professional level.
Integration of Assessment and Intervention Planning
Assessment is intrinsically linked to intervention planning. Data-driven evaluation informs goal setting, selection of strategies, and monitoring of progress. Understanding behavior in context allows practitioners to design interventions that are not only effective but sustainable. For example, identifying the function of disruptive behavior ensures that replacement skills directly address the underlying need, rather than merely suppressing the behavior.
Functional assessment guides intervention choice, while skill acquisition evaluation shapes the developmental trajectory. Combining these insights produces individualized, ethical, and practical plans that respond to each client’s unique profile. Mastery of this integration is a hallmark of BCABA expertise, demonstrating the ability to move seamlessly from observation to analysis to intervention. By embracing a holistic perspective, candidates cultivate a practice that is both scientifically grounded and humanistically informed.
Advanced Strategies in Behavioral Assessment
Beyond basic methodologies, advanced strategies enhance the precision and depth of assessment. Continuous monitoring of trends, consideration of contextual variables, and attention to environmental modifications are essential for nuanced understanding. Sophisticated data analysis techniques allow practitioners to detect subtle shifts in behavior, predict potential challenges, and fine-tune interventions accordingly.
These advanced strategies also include the use of visual data displays, cross-setting comparisons, and sequential analysis of antecedents and consequences. By employing these tools, practitioners gain a multi-layered view of behavior, enhancing both assessment accuracy and intervention effectiveness. Developing expertise in these techniques equips BCABA candidates to approach complex cases with confidence, ensuring that assessments are thorough, actionable, and ethically sound.
The Foundations of Intervention Planning
Intervention planning forms the cornerstone of applied behavior analysis practice. It emerges from a meticulous understanding of assessment data, translating abstract observations into structured, actionable strategies. A proficient practitioner does not merely react to observed behaviors but synthesizes patterns, antecedents, and consequences to craft individualized interventions. This process is iterative, demanding constant refinement as new information surfaces and the client’s response evolves.
Central to intervention planning is the principle of functional assessment. Functional assessment examines why behaviors occur, identifying antecedents that precipitate the action and consequences that maintain it. By comprehending these dynamics, a practitioner can design strategies that address the underlying motivations rather than merely suppressing outward manifestations. This foundational step ensures that interventions are not only effective but ethically aligned with the client’s long-term welfare. The sophistication of intervention planning rests on the ability to integrate empirical evidence with nuanced understanding of individual circumstances.
Reinforcement and Its Multifaceted Applications
Reinforcement remains the most powerful tool in behavior modification. Its application extends beyond simple reward systems into highly nuanced procedures tailored to diverse behavioral targets. Positive reinforcement strengthens behaviors by presenting a desirable outcome, cultivating repetition and mastery. Conversely, negative reinforcement strengthens behavior by removing aversive stimuli, fostering adaptation and persistence in the face of challenges. Mastery of these mechanisms allows practitioners to select reinforcers that resonate with individual preferences while ensuring sustainable behavioral change.
The diversity of reinforcement schedules offers additional versatility. Fixed and variable ratio schedules, interval schedules, and differential reinforcement protocols provide a flexible framework for promoting or diminishing behaviors. For example, variable reinforcement schedules maintain engagement over time and prevent satiation, while differential reinforcement of alternative behaviors can redirect maladaptive actions toward constructive alternatives. Effective deployment of reinforcement demands careful observation, creative tailoring, and continuous evaluation to prevent inadvertent reinforcement of undesired behaviors.
Navigating Punishment and Extinction
Although less frequently applied, punishment and extinction serve pivotal roles in comprehensive intervention strategies. Punishment, whether positive or negative, is intended to decrease the likelihood of undesirable behavior. However, its application necessitates extreme caution due to ethical considerations and the potential for unintended side effects such as emotional distress or avoidance behaviors. Practitioners are trained to reserve punishment for cases where reinforcement-based strategies have proven insufficient, always weighing immediate behavioral suppression against long-term client well-being.
Extinction, defined as the removal of reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior, can produce rapid behavioral shifts. Often, extinction initially triggers a temporary increase in the undesired behavior, termed an extinction burst. Recognizing these phenomena equips practitioners with the foresight to anticipate and manage short-term intensification without reverting to punitive measures. By strategically implementing extinction, behaviors can be reshaped and replaced with adaptive alternatives, enhancing functional skills while minimizing ethical conflicts.
Shaping and Chaining in Skill Acquisition
Complex behaviors often require layered instruction to achieve mastery. Shaping and chaining serve as essential tools in promoting gradual skill development. Shaping involves reinforcing incremental approximations toward a target behavior, creating a trajectory of progressive learning. For instance, teaching a client to articulate complete sentences may begin with reinforcing vocalizations, progressing to word formation, and culminating in structured sentences. This method cultivates gradual mastery while sustaining motivation and engagement.
Chaining, on the other hand, dissects multi-step behaviors into sequential components, reinforcing each step to promote overall skill acquisition. Forward chaining begins with the initial step, sequentially adding subsequent behaviors, whereas backward chaining starts with the final step to ensure immediate reinforcement and a sense of accomplishment. Through careful selection of chaining methodology, practitioners optimize learning efficiency, allowing clients to experience success at each juncture. Together, shaping and chaining provide a versatile framework for teaching complex skills while respecting individual learning rhythms.
The Art of Prompting and Fading
Prompts serve as critical scaffolding for behavior acquisition. Verbal, gestural, and physical prompts guide learners toward desired outcomes while minimizing frustration and confusion. Effective use of prompts demands sensitivity to the client’s developmental level, learning style, and motivational profile. Over-reliance on prompts can inadvertently create dependency, which underscores the importance of systematic fading strategies.
Fading gradually removes prompts as mastery develops, transferring control to natural environmental cues and fostering independence. Stimulus control plays a complementary role, ensuring that behaviors occur in appropriate contexts and generalize beyond the training environment. Discriminative stimuli signal when a behavior is likely to be reinforced, while conditional stimuli facilitate nuanced learning that adapts to varied contexts. Skilled practitioners balance prompt provision and fading to cultivate both competence and autonomy, resulting in lasting behavioral transformation.
Data Collection and Progress Monitoring
The success of any intervention is contingent upon meticulous data collection and progress monitoring. Without empirical tracking, practitioners cannot discern whether strategies are effective or require adaptation. Recording behavioral frequency, duration, intensity, and contextual factors creates a robust foundation for informed decision-making. Graphical representation of data facilitates trend analysis and enhances clarity when communicating progress with caregivers or interdisciplinary teams.
Analyzing variability within behavioral data provides critical insights into the stability of interventions and identifies areas requiring refinement. For instance, fluctuations in engagement may reveal contextual triggers, fatigue effects, or motivational inconsistencies. Practitioners skilled in interpreting these patterns can preemptively adjust strategies, ensuring continuous alignment with client needs. This iterative, data-driven approach underscores the scientific rigor inherent in applied behavior analysis while maintaining flexibility to accommodate individual growth trajectories.
Ethical Integration in Intervention Design
Ethical practice forms the invisible framework underpinning every intervention. Beyond compliance with professional standards, ethical integration encompasses respect for client autonomy, cultural competence, and safeguarding of dignity. Interventions must be conceived with an awareness of potential physical, emotional, and social consequences, prioritizing interventions that promote holistic well-being. Informed consent, transparency, and continuous evaluation for potential harm constitute non-negotiable elements of ethical conduct.
Balancing effectiveness with ethical responsibility often requires nuanced judgment. For instance, a highly effective strategy may be unsuitable if it compromises client autonomy or social inclusion. Practitioners must navigate these tensions with discernment, drawing upon both empirical evidence and compassionate reasoning. By embedding ethical reflection into intervention design, practitioners ensure that behavior change serves the client’s broader life context rather than achieving isolated short-term outcomes.
Integration of Assessment, Planning, and Practice
The hallmark of advanced practice lies in the seamless integration of assessment, intervention, and ethical reasoning. Rather than perceiving these domains as discrete, they function synergistically to produce meaningful, sustainable behavior change. Assessment informs the selection of strategies, which are then implemented through tailored reinforcement, shaping, and prompting. Ongoing monitoring feeds back into this cycle, allowing continuous refinement. Ethical vigilance ensures that every decision is aligned with the client’s long-term welfare, creating a holistic framework for practice.
Expert practitioners demonstrate fluency across these interconnected domains, moving fluidly between data interpretation, strategic planning, and compassionate implementation. This integration reflects both scientific precision and humanistic insight, a duality that defines the essence of professional competence. By mastering the interplay between empirical rigor and ethical stewardship, practitioners cultivate interventions that are both effective and transformative, producing outcomes that resonate across developmental, emotional, and social dimensions.
Understanding Data-Driven Decision-Making in Behavior Analysis
Data-driven decision-making is the keystone of competent behavior analysis. It transcends simple observation and requires a practitioner to translate raw behavior records into actionable insight. Behavior analysts must not only track occurrences but also discern patterns, interpret trends, and implement adjustments grounded in empirical evidence. The ability to accurately interpret data shapes the effectiveness of interventions and ensures that client outcomes align with expected goals. In the realm of BCABA preparation, candidates must hone the skill of converting observational data into practical strategies, bridging the gap between theory and application.
Behavior is dynamic, influenced by a web of environmental, social, and internal factors. The practitioner’s responsibility lies in sifting through this complexity to identify reliable indicators of progress or regression. Data collection is the first step, but analysis transforms these observations into a coherent narrative. Visual representations such as graphs, charts, and timelines offer clarity, highlighting fluctuations that might otherwise go unnoticed. Recognizing a subtle upward trend or an abrupt deviation requires both precision and intuition. The mastery of these skills equips candidates to make informed recommendations that respect the nuanced nature of human behavior.
The Role of Visual Analysis in Detecting Behavior Patterns
Visual analysis is an indispensable tool for interpreting behavioral data. Graphs depicting frequency, duration, latency, or intensity allow practitioners to identify both gradual and sudden changes. These visual cues provide insight into trends, stability, and anomalies, which are essential for making informed intervention decisions. For instance, a consistent upward trajectory in adaptive skills signifies meaningful progress, whereas sudden spikes in maladaptive behavior can indicate environmental disruptions or errors in procedural fidelity.
Understanding the subtleties of visual data requires attention to multiple dimensions. The magnitude of behavior change, the variability between sessions, and the consistency of patterns across contexts all contribute to a practitioner’s interpretation. Candidates must become adept at reading graphs not only for obvious shifts but also for subtle signals that suggest emerging issues or opportunities for intervention refinement. Visual analysis is not an isolated skill; it interacts with contextual knowledge, assessment data, and clinical intuition to guide precise, timely decisions.
Integrating Statistical Measures into Behavioral Interpretation
While visual analysis provides immediate insight, statistical measures complement this approach by quantifying behavior. Metrics such as mean, median, range, and standard deviation describe central tendencies and variability, offering a numerical perspective on behavioral trends. Applying these measures judiciously allows practitioners to differentiate between meaningful changes and random fluctuations, adding rigor to intervention evaluation.
Behavior analysts must exercise discernment when combining statistical and visual data. Numbers alone may obscure contextual nuances, while graphs alone may overlook subtle variations that statistics can reveal. Integrating both approaches enhances the reliability of conclusions, enabling practitioners to select interventions grounded in both quantitative rigor and qualitative observation. The BCABA exam frequently evaluates the ability to navigate this balance, challenging candidates to demonstrate proficiency in interpreting complex datasets and applying findings to real-world behavior scenarios.
Decision-Making Beyond the Numbers
Data interpretation in behavior analysis extends beyond statistical calculations. Decisions are influenced by functional assessment outcomes, fidelity of intervention implementation, and ethical considerations. Evaluating whether to continue, modify, or discontinue a behavioral program requires balancing short-term gains with long-term developmental goals. For example, an intervention that produces immediate behavior reduction but diminishes the client’s overall autonomy may necessitate modification to support sustainable outcomes.
Ethical decision-making intersects with data analysis at multiple levels. Practitioners must avoid bias in interpreting results, resist selective reporting of positive outcomes, and prioritize client welfare above procedural convenience. Every choice, from adjusting session frequency to modifying reinforcement strategies, carries implications for client well-being. Proficient candidates recognize that ethical practice is inseparable from analytical rigor, ensuring that data-driven decisions uphold both efficacy and integrity.
Continuous Monitoring and Fidelity in Interventions
Effective behavior analysis is a dynamic process requiring continuous monitoring. Data collection must be systematic, consistent, and reliable, ensuring that interventions are evaluated accurately over time. Interobserver agreement (IOA) and procedural integrity checks confirm that behavior is recorded accurately and that interventions are implemented as designed. Deviations from expected outcomes may indicate procedural errors, environmental factors, or misinterpretation of functional relationships.
Maintaining fidelity in intervention delivery is critical for interpreting outcomes correctly. Practitioners must observe trends over time, adjusting protocols based on consistent evidence rather than isolated incidents. This ongoing vigilance ensures that interventions remain responsive to client needs and adaptable to changing contexts. Candidates preparing for the BCABA must internalize these practices, understanding that consistent, accurate monitoring is foundational for effective behavior-analytic decision-making.
Developing Analytical Thinking Through Practice
Analytical thinking in behavior analysis is cultivated through deliberate practice. Engaging with case studies, simulating data interpretation, and discussing hypothetical scenarios enhances the ability to recognize subtle patterns and anticipate potential challenges. Practitioners who refine these skills become adept at navigating complex situations, translating raw data into strategic interventions, and responding adaptively when faced with unexpected behavioral shifts.
Developing this analytical mindset requires patience and consistent effort. Candidates should immerse themselves in diverse examples of behavior data, examining outcomes across multiple contexts. By practicing data interpretation, predicting potential complications, and evaluating alternative strategies, candidates strengthen the cognitive flexibility necessary for effective decision-making. This preparation not only bolsters performance on the BCABA exam but also fosters confidence and competence in professional practice.
Ethical Application and Professional Responsibility
Ethical practice is inseparable from data analysis and decision-making. Practitioners are entrusted with client welfare, and every analytic choice must reflect a commitment to ethical standards. Transparent documentation, routine consultation with supervisors, and adherence to professional guidelines reinforce credibility and trustworthiness. Ethical lapses, such as selective reporting or manipulation of outcomes, undermine both the validity of interventions and the reputation of the behavior-analytic field.
Ethics also informs interpretation of complex data patterns. When results are ambiguous, practitioners must weigh evidence carefully, consider potential consequences, and prioritize the client’s best interests. Mastery in this area requires a deep understanding of professional responsibility, integrating analytical precision with moral discernment. Candidates who cultivate ethical rigor alongside analytical skill demonstrate readiness for real-world practice, where decisions have tangible implications for client outcomes and professional integrity.
Leveraging Data for Adaptive Interventions
Data-driven insights allow practitioners to tailor interventions to individual needs, promoting sustainable behavior change. By analyzing trends, identifying triggers, and assessing responsiveness, behavior analysts can adjust reinforcement schedules, environmental modifications, and instructional strategies to optimize outcomes. Adaptive interventions recognize the fluidity of behavior and the importance of context, ensuring that strategies remain effective across diverse situations.
Proficiency in leveraging data extends beyond immediate adjustments. It encompasses proactive planning, predicting potential obstacles, and designing interventions that anticipate developmental trajectories. Candidates who master this skill are capable of implementing strategies that evolve with the client, promoting long-term success and enhancing overall quality of life. The integration of data, ethical judgment, and adaptive planning embodies the essence of advanced behavior analysis practice, setting skilled practitioners apart in both exam performance and professional application.
Understanding the Core of Ethical Practice
Ethical practice in applied behavior analysis transcends the boundaries of examination preparation and becomes the foundation of professional conduct. For BCABA candidates, ethical competence is not merely theoretical; it is a living, evolving practice that informs every intervention and interaction. The intricacies of ethical decision-making often emerge when simple rules collide with real-life complexities. In many cases, principles that seem straightforward may conflict, requiring careful discernment and principled judgment. The professional must recognize the delicate interplay between client welfare, procedural accuracy, and broader societal expectations. Ethical reasoning involves more than adherence to codes; it requires reflection, sensitivity, and a commitment to the well-being of every individual under care. These principles are the bedrock of professional identity and establish the credibility of behavior analysts across diverse practice settings.
Balancing Client Autonomy and Intervention Necessity
A pivotal ethical challenge lies in harmonizing respect for client autonomy with the imperative of effective intervention. Clients may resist certain procedures or strategies even when empirical data supports their efficacy. In these moments, the practitioner must exercise patience, explanation, and negotiation while upholding professional standards. Autonomy does not equate to unbounded choice; rather, it demands a collaborative approach where clients or caregivers are educated on potential outcomes and involved in decision-making. Interventions must be flexible enough to incorporate preferences without compromising safety or effectiveness. Ethical frameworks such as beneficence, which emphasizes promoting welfare, and nonmaleficence, which seeks to prevent harm, guide the professional through these gray areas. Applying these concepts thoughtfully ensures that interventions are respectful, informed, and aligned with evidence-based practice.
Navigating Confidentiality and Professional Boundaries
Confidentiality is the cornerstone of trust between clients and behavior analysts. Maintaining privacy safeguards not only legal compliance but also the emotional safety of individuals and families. Ethical dilemmas arise when circumstances suggest that sharing information could prevent harm or enhance program success. Practitioners must understand where confidentiality ends and where disclosure becomes a moral obligation. Equally critical are professional boundaries, which govern interactions with clients, families, and colleagues. Avoiding dual relationships, managing potential conflicts of interest, and sustaining impartial judgment are essential for ethical practice. Professionals must resist pressures that could compromise objectivity, recognizing that integrity is reinforced by consistent adherence to these boundaries. The subtle balance between confidentiality, transparency, and relational respect demands ongoing vigilance and reflection.
Ethical Considerations in Data Management
Data is the lifeblood of applied behavior analysis, yet ethical concerns often emerge in its collection, reporting, and interpretation. Requests to manipulate, omit, or selectively report outcomes present profound challenges. Adhering to accurate and comprehensive documentation protects the client and upholds the scientific integrity of interventions. Ethical data management requires a commitment to transparency, objectivity, and evidence-based practice. Professionals must exercise judgment when external pressures conflict with these standards, prioritizing the welfare of the client above convenience or expediency. Recognizing the weight of these decisions cultivates a professional ethos grounded in honesty, accountability, and dedication to outcomes that are both meaningful and measurable.
Integrating Cultural Competence into Ethical Practice
Cultural competence is inseparable from ethical responsibility. Behavior analysts work within diverse communities, each with unique norms, values, and expectations. Intervention strategies must align with cultural context to avoid unintended harm and to enhance effectiveness. Practitioners must actively engage in learning about the traditions, beliefs, and preferences of clients and families. Ethical practice involves listening, adapting, and designing interventions that honor cultural identity while achieving measurable progress. Sensitivity to language, social dynamics, and community norms strengthens both rapport and outcomes. Professional judgment in this domain extends beyond technical expertise to include empathy, respect, and a nuanced understanding of human diversity. Ethical adherence in culturally diverse settings enhances relevance, trust, and overall intervention success.
Applying Professional Judgment in High-Stakes Situations
Professional judgment is the linchpin that connects knowledge, ethics, and practical action. It encompasses the ability to anticipate consequences, weigh alternatives, and select strategies that uphold both client well-being and scientific principles. High-stakes scenarios, such as managing dangerous behaviors or critical developmental challenges, demand careful integration of assessment data, intervention strategies, and ethical reasoning. Professionals must evaluate options for safety, efficacy, and long-term benefit, resisting shortcuts or overly restrictive measures. The BCABA examination frequently presents situations where technically correct options exist, but only those aligned with ethical standards represent the optimal choice. Developing this skill requires repeated practice, reflective thinking, and conscious application of professional principles in daily practice.
Mentorship and Collaborative Ethical Reasoning
Ethical reasoning is enriched by mentorship, supervision, and collaboration. Consulting experienced professionals in ambiguous situations provides insight into diverse approaches and reinforces sound decision-making. Mentorship allows emerging behavior analysts to observe nuanced applications of ethical principles, learn from real-world challenges, and refine their judgment. Reflection, dialogue, and feedback deepen understanding, transforming abstract rules into actionable strategies. Ethical proficiency grows through experience, discussion, and exposure to complex scenarios that cannot be captured in textbooks alone. By embracing collaboration and seeking guidance, BCABA candidates cultivate a resilient framework for decision-making that serves both the client and the professional community.
The Role of Reflection in Continuous Ethical Development
Reflection is an ongoing process that strengthens ethical competence. Professionals must regularly assess their decisions, interventions, and interactions to ensure alignment with both client needs and ethical standards. Reflective practice involves examining outcomes, identifying areas for improvement, and considering alternative approaches for future application. It encourages humility, self-awareness, and accountability, fostering a culture of continuous growth. For BCABA candidates, reflective habits prepare them to navigate unforeseen ethical challenges with confidence and poise. This iterative process transforms knowledge into wisdom, allowing practitioners to act decisively while remaining responsive to evolving circumstances. Reflection solidifies ethical foundations and cultivates professional resilience across the dynamic landscape of applied behavior analysis.
Promoting Ethical Culture Within Practice Settings
Creating a culture of ethical excellence extends beyond individual competence to organizational responsibility. Behavior analysts influence their teams, agencies, and communities by modeling integrity, transparency, and principled decision-making. Promoting open discussion of ethical dilemmas, establishing clear expectations, and providing ongoing training fosters a professional environment that prioritizes client welfare and accountability. Ethical culture encourages proactive identification of potential conflicts, supports consistent documentation standards, and validates culturally responsive interventions. Professionals who engage actively in shaping such cultures contribute to sustainable, high-quality practice that benefits clients, colleagues, and the broader behavioral health field. Cultivating ethical culture requires dedication, leadership, and a commitment to shared values that transcend day-to-day operational pressures.
The Interplay of Ethics, Science, and Human Values
Applied behavior analysis exists at the intersection of empirical science and human experience. Ethical practice is not merely procedural compliance; it involves harmonizing measurable outcomes with compassion, respect, and moral consideration. The interplay between rigorous scientific methods and human values challenges practitioners to consider long-term impact, quality of life, and dignity in every decision. Ethical behavior analysts navigate tensions between efficiency and empathy, data and lived experience, ensuring that interventions are both effective and morally sound. Professional judgment in this context requires balancing evidence-based approaches with the nuances of individual human stories, recognizing that science serves humanity rather than the reverse. Ethical awareness, therefore, becomes a dynamic process of aligning methodology, integrity, and empathy in service of meaningful progress.
Developing Resilience Through Ethical Mastery
The journey toward ethical mastery demands resilience, perseverance, and reflective adaptability. Behavior analysts encounter continuous challenges that test their judgment, patience, and commitment to principles. Successfully navigating complex ethical landscapes strengthens confidence, enhances credibility, and deepens professional satisfaction. BCABA candidates who cultivate resilience through ethical practice emerge prepared to manage diverse situations with clarity and composure. Resilient professionals anticipate dilemmas, respond thoughtfully under pressure, and integrate lessons from each experience into future decision-making. Ethical mastery, therefore, is both a skill and a mindset, reinforcing the capacity to provide interventions that are safe, effective, and aligned with the highest standards of moral and scientific integrity.
Structured Strategies for Exam Preparation
The journey toward BCABA mastery begins with a methodical approach to preparation, where every study session is deliberately structured to maximize retention and understanding. Beyond superficial memorization, candidates must cultivate a system of active engagement with the material, internalizing concepts through repeated exposure and purposeful practice. This involves dissecting foundational principles, examining applied case studies, and exploring practical scenarios that mirror real-world applications. When knowledge is approached as a living, interconnected framework, rather than isolated facts, it becomes easier to retrieve under the pressure of the exam.
Active learning strategies amplify comprehension. Teaching complex concepts to a peer or articulating thought processes aloud fosters deeper understanding, as the brain is forced to organize information logically. This method often reveals nuances that passive reading overlooks, helping candidates detect subtle distinctions in behavior analysis that are critical for high-level performance. Visualization techniques, including imagining oneself implementing interventions or analyzing client data, further enhance cognitive assimilation. The combination of active articulation, scenario simulation, and repetitive review cultivates an ingrained familiarity that transforms knowledge into instinctive skill.
A crucial component of structured preparation is the segmentation of study material into manageable modules. Tackling content in defined portions, whether by behavioral principles, assessment techniques, or ethical frameworks, ensures comprehensive coverage without cognitive overload. Regular intervals of focused study followed by brief periods of reflection allow information to consolidate effectively, strengthening long-term retention. By transforming study into an intentional, organized process, candidates develop not only competence but also confidence, fostering a sense of preparedness that translates directly into exam performance.
Mastering Practice Exams
Practice exams function as a crucible for knowledge application, providing candidates with the opportunity to synthesize information under realistic testing conditions. These exercises serve a dual purpose: they familiarize the examinee with exam format and pacing while simultaneously identifying areas of weakness. Encountering varied scenarios repeatedly exposes gaps in understanding, enabling targeted review that mitigates potential pitfalls.
Analysis of incorrect responses is especially enlightening. Common mistakes, such as misattributing antecedent-behavior-consequence relationships or overlooking ethical considerations, become apparent when answers are dissected systematically. Each error represents an opportunity for recalibration, allowing candidates to refine reasoning strategies and strengthen analytical accuracy. The cumulative effect of iterative practice is the development of rapid pattern recognition and intuitive decision-making, essential traits for navigating the nuanced challenges presented by the BCABA exam.
Simulated timed conditions also cultivate essential time management skills. Candidates learn to allocate cognitive resources efficiently, balancing rapid assessment with thoughtful deliberation. By repeatedly navigating full-length examinations, the pressure of the timed environment becomes familiar, reducing anxiety and enhancing confidence. Practice exams transform abstract preparation into concrete experience, enabling candidates to approach the real exam with both mental readiness and strategic foresight.
Precision in Time Management
Effective time management is not merely about completing questions promptly; it requires strategic distribution of focus to maximize accuracy and efficiency. Exam scenarios often vary in complexity, demanding careful evaluation of each component before selecting a response. Some questions present multiple plausible solutions, requiring the examinee to weigh consequences, analyze data, and integrate ethical considerations. Hasty choices may compromise correctness, whereas deliberate pacing ensures thoughtful analysis.
Allocating time according to question type and perceived difficulty allows candidates to maintain steady progress without becoming mired in challenging sections. Implementing mental checkpoints, such as reviewing remaining time at intervals or segmenting the exam into clusters, supports a rhythm of steady advancement. Practicing pacing strategies during preparation, especially through timed mock exams, equips candidates with the ability to navigate the actual test without succumbing to pressure-induced errors. Mastery of time management thus becomes both a skill and a safeguard, enhancing accuracy while minimizing stress.
Equally important is the cultivation of adaptive flexibility. Some scenarios demand rapid shifts in analytical perspective, such as reinterpreting ambiguous data or reconsidering intervention strategies. Candidates trained to recognize such inflection points can pivot seamlessly, maintaining clarity and coherence in their reasoning. Time management is therefore not merely mechanical—it intertwines with cognitive agility, reflecting the integration of knowledge, strategy, and self-awareness.
Cultivating a Mastery Mindset
Exam success hinges as much on mindset as on factual knowledge. A mastery-oriented perspective transforms challenges into opportunities for skill development rather than threats to performance. Candidates with this mindset focus on the application of principles, approaching questions as real-world problems requiring thoughtful solutions. This orientation reduces anxiety, encourages active engagement, and fosters resilience in the face of complex or ambiguous scenarios.
Maintaining calm under pressure is essential. Techniques such as deep breathing, cognitive reframing, and positive visualization mitigate stress responses, allowing mental resources to focus fully on analysis rather than apprehension. Visualizing successful engagement with exam material reinforces confidence and prepares the mind to execute strategies fluidly. Mindset also intersects with preparation habits: those who view challenges as iterative learning opportunities tend to engage more deeply with content, seek clarification when necessary, and refine reasoning skills consistently.
Emphasizing process over outcome reinforces mastery thinking. Instead of fixating on achieving perfect scores, candidates concentrate on internalizing methodologies, honing judgment, and cultivating analytical rigor. This orientation nurtures both competence and self-assurance, enabling examinees to approach each scenario with deliberate reasoning, ethical consideration, and confidence in their abilities.
Integrating Scenario Interpretation Skills
A defining feature of the BCABA exam is its reliance on scenario-based questions, which require integration of assessment, intervention, and ethical reasoning. Mastery in this area involves systematic processing: identifying antecedents, discerning behavior functions, evaluating intervention options, and considering ethical implications. Training oneself to approach scenarios with methodical consistency enhances both speed and accuracy.
Scenario analysis is strengthened by repeated exposure to varied case types. Simulating real-world client situations, whether through practice questions or applied exercises, cultivates an instinct for recognizing patterns, predicting outcomes, and selecting contextually appropriate interventions. Over time, candidates develop an intuitive understanding of behavioral dynamics, enabling them to navigate complex questions efficiently. Integrating ethical reasoning into this process is equally vital, as decisions must reflect not only technical correctness but also adherence to professional standards.
Developing scenario fluency also relies on connecting theory to practice. Rather than treating principles as abstract, candidates benefit from envisioning their application in realistic contexts. This habit transforms conceptual knowledge into actionable insight, supporting both exam performance and future professional practice. By consistently engaging with case-based material, examinees acquire a versatile toolkit for analytical reasoning, enhancing both confidence and competence.
The Role of Holistic Self-Care
Preparation extends beyond intellectual effort; physical and mental well-being underpin cognitive performance. Adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and restorative activities bolster attention, memory, and decision-making capabilities. The demands of the BCABA exam require sustained focus, rapid problem-solving, and careful analysis under pressure, all of which are optimized when the mind and body are nourished and rested.
Self-care also enhances resilience. Study schedules that include breaks, physical activity, and relaxation techniques prevent burnout, allowing for consistent, high-quality engagement with material. Mental rest facilitates consolidation of learned information, transforming short-term memory into long-term retention. Candidates who integrate self-care into their preparation demonstrate not only knowledge mastery but also the ability to maintain clarity, composure, and effectiveness during high-stakes testing situations.
Moreover, holistic self-care supports emotional regulation, enabling candidates to navigate uncertainty and challenge with poise. The intersection of physical well-being, mental clarity, and emotional balance creates a foundation upon which mastery is built, ensuring that preparation is both sustainable and effective.
Ethical Acumen and Professional Readiness
Ethics form a cornerstone of the BCABA examination and professional practice. Candidates must consistently integrate ethical reasoning into every aspect of decision-making, from data interpretation to intervention selection. Recognizing potential conflicts, understanding boundaries, and applying professional standards are essential skills that extend beyond the exam into real-world client interactions.
Developing ethical acumen involves deliberate reflection on case scenarios, considering multiple perspectives and potential consequences. Candidates benefit from reviewing professional codes, evaluating complex dilemmas, and exploring nuanced situations where ethical clarity is required. Embedding this focus into study habits ensures that ethical reasoning becomes automatic, enhancing both exam performance and professional competence.
Professional readiness extends beyond ethical proficiency to include analytical rigor, applied knowledge, and scenario fluency. Candidates who cultivate these dimensions simultaneously are equipped not only to succeed on the BCABA exam but also to engage meaningfully in client-centered practice. The integration of technical skill, ethical judgment, and reflective insight forms the essence of holistic preparation, aligning exam mastery with real-world impact.
Conclusion
Preparing for the BCABA exam is a journey that blends knowledge, skill, and ethical judgment. From understanding foundational principles of behavior to mastering assessment strategies, designing effective interventions, analyzing data, and navigating complex ethical scenarios, every step builds the competence required for professional excellence. This series has provided a roadmap, offering practical insights, insider tips, and a mindset geared toward mastery.
Success on the BCABA exam is more than memorization; it is the ability to integrate concepts, think critically, and apply knowledge to real-world situations. Active engagement with study material, strategic practice, and reflective learning create a foundation that goes beyond passing the exam—it equips you to make meaningful, positive impacts in the lives of clients. Ethical reasoning, cultural sensitivity, and professional judgment are not just exam topics—they are the hallmarks of a skilled and compassionate practitioner.
By approaching preparation systematically, practicing consistently, and maintaining a confident, focused mindset, candidates position themselves not only to succeed on the exam but to thrive in their careers. The journey may be challenging, but every step offers growth, insight, and the opportunity to contribute meaningfully to the field of behavior analysis. With dedication, preparation, and a mastery-oriented mindset, BCABA certification becomes more than a goal—it becomes a milestone in a rewarding and impactful professional journey.