Exam Code: 1D0-437
Exam Name: CIW Perl Fundamentals
Certification Provider: CIW
Corresponding Certifications: CIW Perl Specialist, CIW Web Development Professional, Master CIW Enterprise Developer
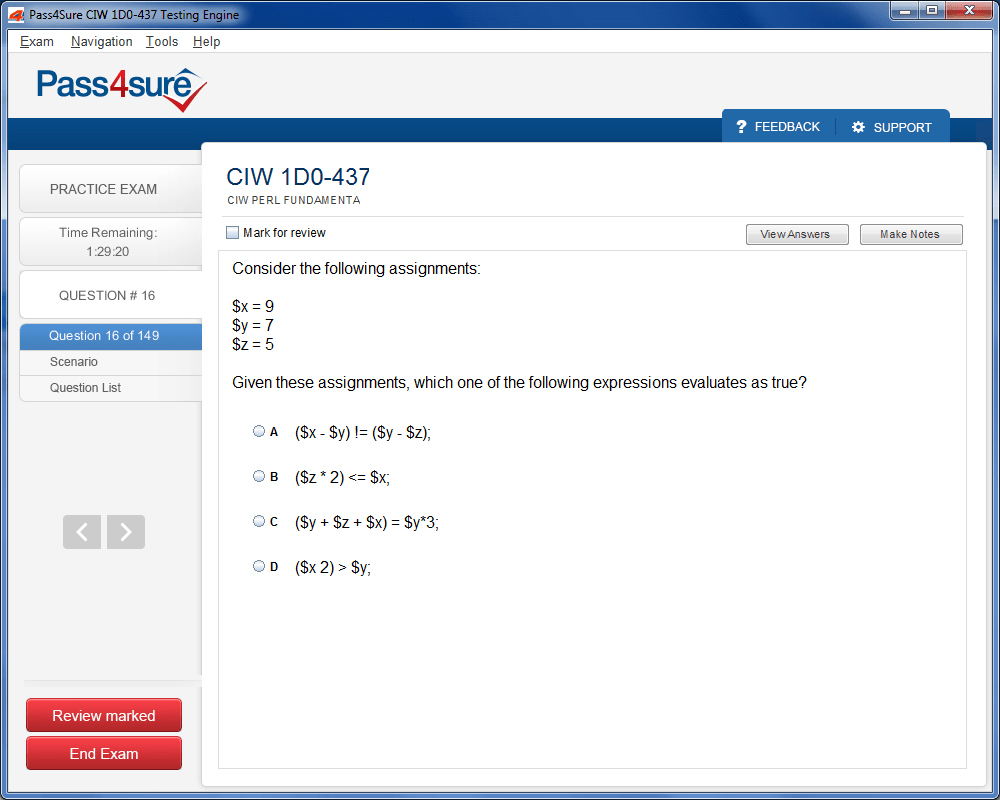
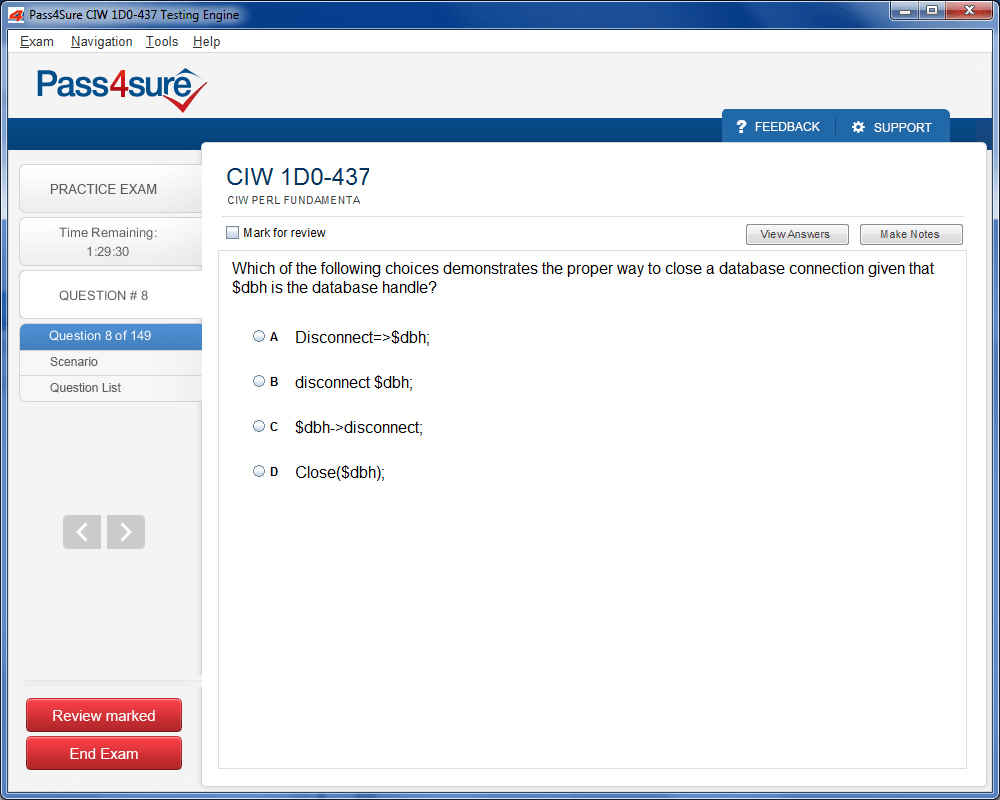
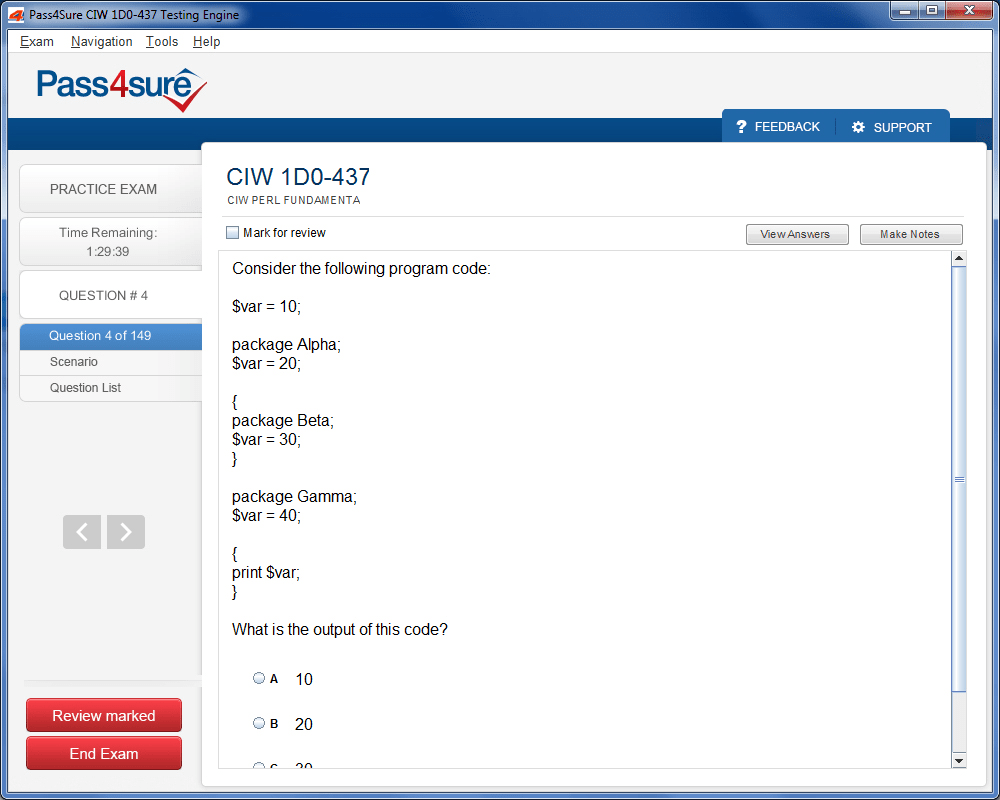
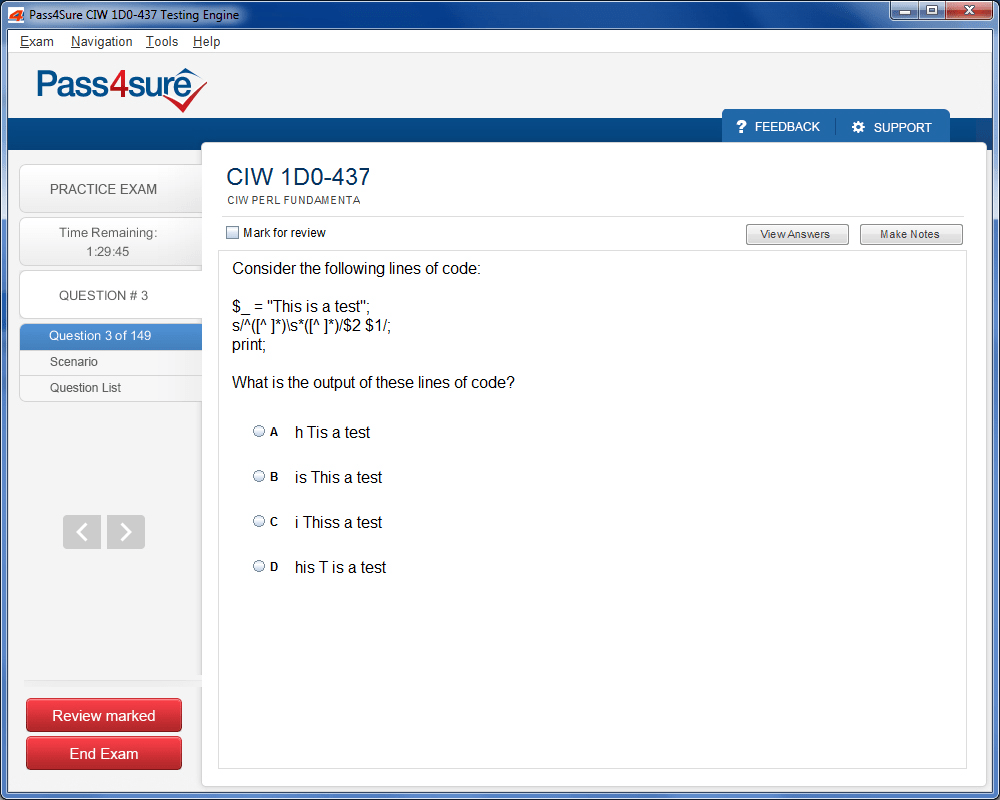
1D0-437 Exam Product Screenshots
Frequently Asked Questions
How does your testing engine works?
Once download and installed on your PC, you can practise test questions, review your questions & answers using two different options 'practice exam' and 'virtual exam'. Virtual Exam - test yourself with exam questions with a time limit, as if you are taking exams in the Prometric or VUE testing centre. Practice exam - review exam questions one by one, see correct answers and explanations.
How can I get the products after purchase?
All products are available for download immediately from your Member's Area. Once you have made the payment, you will be transferred to Member's Area where you can login and download the products you have purchased to your computer.
How long can I use my product? Will it be valid forever?
Pass4sure products have a validity of 90 days from the date of purchase. This means that any updates to the products, including but not limited to new questions, or updates and changes by our editing team, will be automatically downloaded on to computer to make sure that you get latest exam prep materials during those 90 days.
Can I renew my product if when it's expired?
Yes, when the 90 days of your product validity are over, you have the option of renewing your expired products with a 30% discount. This can be done in your Member's Area.
Please note that you will not be able to use the product after it has expired if you don't renew it.
How often are the questions updated?
We always try to provide the latest pool of questions, Updates in the questions depend on the changes in actual pool of questions by different vendors. As soon as we know about the change in the exam question pool we try our best to update the products as fast as possible.
How many computers I can download Pass4sure software on?
You can download the Pass4sure products on the maximum number of 2 (two) computers or devices. If you need to use the software on more than two machines, you can purchase this option separately. Please email sales@pass4sure.com if you need to use more than 5 (five) computers.
What are the system requirements?
Minimum System Requirements:
- Windows XP or newer operating system
- Java Version 8 or newer
- 1+ GHz processor
- 1 GB Ram
- 50 MB available hard disk typically (products may vary)
What operating systems are supported by your Testing Engine software?
Our testing engine is supported by Windows. Andriod and IOS software is currently under development.
Mastering CIW 1D0-437: Your Guide to Perl Fundamentals Certification
Perl’s syntax can be likened to a linguistic kaleidoscope, where symbols, operators, and constructs converge to form a tapestry of expressive capability. Unlike conventional languages that impose rigid grammatical structures, Perl invites coders to wield its syntax with dexterity, transforming ordinary scripts into sophisticated instruments of automation. Scalar variables, arrays, and hashes serve not merely as containers but as vessels for intricate manipulations of textual and numerical data. Mastery of these constructs allows developers to craft solutions that are both concise and powerful.
Regular expressions, the crown jewel of Perl, elevate text processing to a quasi-artistic endeavor. These patterns, intricate yet precise, empower developers to discern structures hidden within strings, enabling data extraction, validation, and transformation with astonishing efficiency. For those delving into web applications, this capability is indispensable: user inputs can be sanitized, logs parsed, and dynamic content generated with surgical precision. The subtleties of greedy versus non-greedy matching, lookahead assertions, and backreferences offer layers of sophistication that reward meticulous study.
Perl’s semantics, often overlooked by novices, embody an ethos of pragmatism. Context sensitivity, for instance, dictates how expressions behave, allowing a single line of code to produce varying outcomes depending on its scalar or list context. This polymorphic behavior encourages developers to consider not just the mechanics of execution but the philosophical underpinnings of expression, fostering a mindset attuned to elegance and efficiency.
Modularization and Reusability in Perl Programming
The architecture of Perl thrives on modularization, a principle that transforms chaotic codebases into maintainable frameworks. By encapsulating functionality within modules, developers can decouple concerns, facilitate testing, and enhance readability. This modular approach resonates profoundly with the objectives of web development, where disparate components—databases, APIs, and user interfaces—must interact seamlessly.
Perl’s Comprehensive Module Archive (CPAN) serves as an unparalleled repository of reusable code, spanning cryptography, network protocols, and GUI development. Integrating CPAN modules allows developers to circumvent reinventing the wheel, channeling their creativity into higher-order problem-solving. For aspiring professionals, leveraging these resources demonstrates both technical acumen and strategic efficiency, hallmarks of expert craftsmanship.
Subroutines, another cornerstone of modularity, epitomize Perl’s ability to abstract complex operations. By encapsulating recurring logic into named routines, scripts gain clarity, maintainability, and adaptability. This abstraction not only streamlines development but also cultivates a disciplined mindset, reinforcing best practices in coding and architecture.
Perl in Dynamic Web Content Generation
In the dynamic ecosystem of web development, Perl functions as both artisan and engineer, orchestrating content generation with dexterous precision. When interfacing with HTML forms, scripts, and databases, Perl transforms raw data into structured, actionable intelligence. Its CGI capabilities, though evolved over decades, remain potent tools for crafting interactive web experiences.
Data validation, a perennial challenge in web applications, benefits immensely from Perl’s expressive operators and pattern-matching capabilities. Erroneous inputs can be intercepted with nuance, ensuring data integrity while minimizing computational overhead. Beyond validation, Perl facilitates session management, cookie handling, and templating, enabling developers to construct personalized, responsive experiences for end-users.
Perl’s proficiency extends to integration with relational and non-relational databases. Through DBI and related modules, scripts can execute complex queries, manage transactions, and orchestrate relational schemas with minimal syntactic overhead. This interplay between Perl and databases underscores the language’s role as a bridge between static markup and dynamic, data-driven functionality.
Automation and Task Orchestration with Perl
One of Perl’s most celebrated domains is automation, where the language’s versatility manifests in unparalleled productivity. System administrators and web developers alike harness Perl to automate repetitive processes, manipulate files, and interface with operating system utilities. Cron jobs, file parsing scripts, and network monitoring routines exemplify its utility in operational orchestration.
The language’s natural affinity for string and file handling renders it ideal for log analysis and report generation. By leveraging Perl, developers can distill vast quantities of unstructured data into actionable insights, enhancing operational visibility and decision-making. This capability, though deceptively simple, is a cornerstone of efficient, scalable web systems.
Perl’s automation potential is magnified when combined with external APIs and network protocols. Scripts can retrieve, parse, and manipulate remote data streams, enabling web applications to function as interconnected nodes in a larger digital ecosystem. Such sophistication underscores the language’s enduring relevance, even amidst the proliferation of contemporary scripting technologies.
Advanced Perl Techniques for Expert Practitioners
For the seasoned Perl practitioner, mastery extends beyond foundational syntax into realms of introspection, dynamic execution, and meta-programming. Auto-loading modules, symbolic references, and advanced regular expression techniques enable scripts to adapt and evolve at runtime, providing unprecedented flexibility in complex applications.
Exception handling, a vital aspect of resilient programming, is elegantly supported in Perl. By employing eval blocks and structured error management, developers can anticipate and mitigate failures, ensuring robustness and continuity in web services. Coupled with logging mechanisms and diagnostic modules, these practices cultivate code that is both fault-tolerant and maintainable.
Furthermore, Perl’s capacity for text transformation is enhanced through sophisticated encoding and decoding strategies. From Unicode normalization to MIME handling, scripts can process diverse character sets and formats, ensuring global applicability of web applications. Such attention to linguistic nuance and data fidelity elevates Perl from a mere scripting language to a refined instrument of digital craftsmanship.
Perl’s scalar variables serve as the atomic units of computation, encapsulating singular entities with an almost chameleonic capacity. These constructs can oscillate between numeric calculation and string manipulation without ceremony, a fluidity seldom encountered in statically typed languages. Scalars are conduits for both ephemeral values and enduring references, bridging transient computations and persistent data structures. The elegance lies not merely in storing a number or a string but in the nuanced orchestration of operations that respect context and type simultaneously.
Arrays, by contrast, embody ordered sequences, a lattice upon which iterative logic thrives. Each element resides in a temporal continuum within the array, accessible through indices that begin at zero. Yet the true puissance of arrays emerges when juxtaposed with Perl’s contextual intelligence: a scalar assignment can transform into a count, while list operations permit cascading transformations with minimal syntactic verbosity. Iteration constructs like foreach or the terse implicit loops allow arrays to become both narrative and functional instruments, weaving data into patterns that are simultaneously predictable and dynamic.
Hashes are perhaps the most polymorphic of Perl’s core types, translating keys into values with remarkable efficiency. They manifest associative memory, allowing developers to map linguistic tokens, numerical identifiers, or symbolic constructs into coherent datasets. The hash’s capacity for rapid lookup, coupled with the flexibility to manipulate both keys and values in situ, invites inventive algorithms and concise coding paradigms. The interplay of arrays and hashes often evokes a symphonic quality, where the programmer orchestrates data flows with both precision and artistry.
Contextual Nuances and the Scalar-List Dichotomy
Perl’s genius is entwined with its sensitivity to context, a feature that endows even elementary expressions with multilayered interpretation. Scalar context reduces computations to singular, definitive values, while list context propagates multiplicities, a duality that imbues scripts with adaptive intelligence. For novices, this characteristic can appear arcane, yet it underpins some of Perl’s most compelling idioms. Calculating the length of an array, extracting elements, or manipulating ranges becomes an exercise in contextual choreography. The language, in essence, encourages a mental elasticity, urging programmers to anticipate multiple interpretive layers simultaneously.
Contextual awareness extends beyond mere arithmetic or data extraction; it infiltrates operator behavior, function return values, and control structures. The interplay between scalar and list contexts can be exploited to condense verbose logic into elegant expressions, rendering Perl not just a programming tool but a medium for concise expression. This duality, while initially disorienting, cultivates an aptitude for abstraction and strategic thinking, qualities prized in professional and certification landscapes alike.
Operators as Artifacts of Transformation
The operator landscape in Perl transcends conventional arithmetic and logical boundaries, incorporating tools designed for textual transmutation and pattern cognition. Concatenation, regular expression matching, substitution, and transliteration operators allow text to be treated as malleable substance rather than static data. This malleability is critical in scenarios ranging from log parsing to natural language processing, where patterns often eclipse raw numbers in significance.
Perl’s operator hierarchy and precedence rules demand rigorous attention, as the language affords both brevity and peril in equal measure. A misapplied operator can invert logic, truncate arrays, or produce subtle runtime anomalies. Conversely, mastery unlocks a syntax that reads almost narratively, where expressions communicate intention as much as functionality. Such operators, when coupled with contextual sensitivity, become instruments of cognitive leverage, permitting developers to encode sophisticated logic with minimal syntactic encumbrance.
Control Structures and the Elegance of Flow
Beyond the rudimentary loops and conditionals familiar to any programmer, Perl introduces constructs that embody both utility and whimsy. The flip-flop operator, for instance, permits sequential stateful evaluations without resorting to verbose conditional scaffolding. Implicit loops, such as those embedded within file reading or pattern matching routines, further reduce syntactic friction, allowing the code to resonate with clarity rather than ceremony.
Logical branching in Perl can be sculpted into forms that are simultaneously terse and expressive, a testament to the language’s design philosophy. Conditional expressions, when combined with operators sensitive to context, enable the developer to articulate nuanced decision-making pathways. Iterative constructs, both explicit and implicit, encourage a rhythm in coding that parallels musical phrasing, transforming procedural execution into a narrative cadence.
Subroutines: Modularity and Cognitive Architecture
Subroutines in Perl are the scaffolding upon which complex scripts are constructed. By encapsulating repetitive logic, they foster maintainability, clarity, and adaptability. Each subroutine can be conceived as a cognitive module, processing inputs, generating outputs, and abstracting away complexity. Parameters are not mere placeholders; they become instruments for disciplined communication between disparate segments of code, enabling an architecture that is simultaneously modular and coherent.
The creation of reusable subroutines aligns closely with professional best practices and certification competencies, emphasizing clarity of interface, predictable behavior, and robust error handling. Beyond practical utility, subroutines cultivate a mindset attuned to decomposition, abstraction, and strategic reuse—skills that extend far beyond Perl itself. In essence, the disciplined use of subroutines transforms raw code into an organized symphony, where each function contributes harmoniously to the overarching logic.
Experimental Flourishes and Data Manipulation
Perl’s inherent flexibility encourages experimentation, rewarding curiosity with potent results. Edge cases, unconventional data structures, and recursive subroutines invite exploration, turning the language into a laboratory for cognitive exploration. Arrays and hashes can be interwoven in imaginative ways, their elements transformed, filtered, and aggregated with expressive operators that act as both scalpel and paintbrush.
Manipulating data creatively in Perl cultivates a skill set that is simultaneously analytical and aesthetic. Patterns emerge not only from explicit instructions but from the dynamic interplay of context, operator behavior, and structural choices. The language’s permissiveness, when guided by disciplined reasoning, facilitates a form of cognitive artistry—an arena where programming and inventive problem-solving coalesce seamlessly.
The Alchemy of Pattern Synthesis
Regular expressions in Perl resemble an arcane art more than mere coding. They allow the conjuration of patterns that can morph, split, and transmute strings with almost magical dexterity. The act of defining a pattern is akin to weaving a tapestry, where each literal, wildcard, or quantifier threads the fabric of the string universe. Understanding this alchemy is indispensable for practitioners seeking not merely functional, but elegant, and efficient solutions.
The substratum of pattern synthesis lies in the dexterity to combine elementary constructs into intricate sequences. Character classes act as the palette, defining the spectrum of acceptable inputs. Quantifiers modulate the intensity, prescribing the rhythm and frequency of matches, while anchors dictate the spatial orientation of the search. When orchestrated with grouping and backreferences, these elements coalesce into a symphony capable of decoding labyrinthine datasets or verifying multifaceted input structures.
Non-Greedy Logic and Temporal Parsing
A frequent stumbling block for novices is the greediness inherent in regex quantifiers. By default, they grasp as much of the string as possible, potentially overshooting the desired match. Non-greedy constructs counteract this, instructing the engine to capture minimally necessary substrings. This subtle yet profound adjustment transforms pattern matching from brute force to surgical precision.
Temporal parsing, in turn, relies heavily on such control. Log files, temporal sequences, and structured records often contain recurring motifs where selective extraction is paramount. By leveraging non-greedy quantifiers in tandem with lookahead and lookbehind assertions, developers can isolate segments of interest without perturbing surrounding data. This methodology is especially potent when parsing nested or hierarchical content where conventional matching falters.
Substitution as Transformational Conduit
Pattern matching attains its full potential when coupled with substitution. Perl’s s/// operator is not a mere replacement mechanism but a transformational conduit. Through intricate expressions, strings can be sanitized, reformatted, or repurposed. For instance, malformed input can be normalized, tokens extracted and rearranged, or textual anomalies rectified with minimal overhead.
The true power emerges when substitution is contextual. Conditional replacements allow different segments to be transformed according to local patterns, enabling dynamic and intelligent string manipulation. This is particularly valuable in web applications, where inputs vary widely yet must adhere to rigid structural rules, such as in CIW 1D0-437 practical scenarios.
Synergistic Integration with Data Structures
Regular expressions achieve maximal utility when harmonized with Perl’s core data structures. Captured groups, when stored in hashes, transform ephemeral matches into retrievable knowledge, supporting rapid lookup or aggregation. Arrays facilitate iterative processing, allowing patterns to be applied over sequences with minimal repetition and maximal readability. Subroutines, meanwhile, modularize regex logic, fostering reuse and abstraction while adhering to principles of maintainable code.
This synergy mirrors Perl’s philosophical essence: a confluence of pragmatism and ingenuity. Complex data manipulations that might require extensive procedural logic in other languages can be condensed into concise, readable expressions in Perl. Mastery of these integrations distinguishes the adept from the merely competent, particularly for those preparing for high-stakes certification or enterprise-level data processing.
Lookahead and Lookbehind: Conditional Insight
Assertions like lookahead and lookbehind expand pattern matching into a domain of conditional insight. Unlike standard matches, they do not consume characters; instead, they assert the presence or absence of specific contexts. Positive assertions confirm the existence of conditions ahead or behind the current position, while negative assertions forbid them, yielding precise, context-aware matching.
These constructs are invaluable when parsing data streams with embedded rules or hierarchical dependencies. For instance, extracting attributes from HTML elements, isolating metadata from file headers, or validating conditional formats in user input all benefit from the nuanced logic afforded by assertions. In essence, they allow patterns to “think ahead” or “remember behind,” creating a temporal dimension in textual analysis.
Recursive and Conditional Patterns
Advanced Perl regexes transcend linear parsing, enabling recursion and conditional logic within patterns. Recursive patterns allow self-referential matching, ideal for nested structures such as parentheses, JSON-like blocks, or hierarchical configurations. Conditional patterns introduce branching logic, altering behavior based on prior captures or assertions.
Together, these features cultivate a microcosm of computational reasoning inside the regex engine. Developers can encode complex parsing algorithms directly within pattern expressions, reducing external procedural code while enhancing clarity and efficiency. For certification aspirants, familiarity with these constructs represents the pinnacle of regex proficiency, offering solutions to otherwise intractable problems.
Experiential Pedagogy for Pattern Mastery
Proficiency in pattern matching is rarely bestowed by theoretical study alone. Practical engagement, experimentation, and iterative refinement cultivate intuition and skill. Crafting scripts to validate email formats, parse server logs, or transform textual datasets embeds knowledge through experience. Observing the interplay between quantifiers, assertions, and grouping elucidates the subtleties of Perl’s regex engine.
By progressively escalating complexity, practitioners develop an eye for elegant patterns, minimizing redundancy and optimizing efficiency. Such iterative exploration transforms regex from a procedural tool into a lens for conceptualizing and manipulating data, aligning with both practical certification goals and real-world programming exigencies.
The Arcane Nuances of File Access in Perl
Perl’s prowess in file handling is seldom appreciated solely for its superficial syntax; beneath its seemingly quotidian operations lies a latticework of intricacies that reward meticulous attention. Opening a file is not merely a mechanical invocation of open statements; it is a deliberate act requiring consideration of access modes, encodings, and potential race conditions. The subtle interplay between read, write, and append operations can determine the robustness of a script, especially when handling ephemeral log files that fluctuate in size or content unpredictably. Advanced practitioners often incorporate conditional checks that preemptively assess file existence and permissions, ensuring scripts transcend rudimentary failures to achieve resilience.
Perambulating Through Data Streams
Reading files in Perl is an exercise in controlled perambulation through streams of textual information. Scripts can navigate sequentially, line-by-line, for granular inspection, or ingest entire corpuses into memory for comprehensive analysis. This flexibility proves indispensable when parsing complex server logs, extracting irregular patterns, or transforming semi-structured data into coherent formats. The ability to marshal these streams, filter out superfluous noise, and isolate semantically rich fragments reflects a synthesis of both algorithmic rigor and linguistic sensitivity, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence.
The Esoteric Craft of File Mutation
Writing to files in Perl is an esoteric craft, demanding both foresight and precision. Overwriting a file is deceptively simple but fraught with peril if executed without preemptive validation. Appending, conversely, enables incremental accumulation of insights, producing a temporal narrative of system behavior or user interaction. The subtle art lies in combining these operations with buffering strategies, ensuring efficiency while mitigating the risk of incomplete writes. Such practices echo the attention to detail revered in CIW 1D0-437 preparation, where scripts are expected to operate reliably under duress, maintaining fidelity of both data and structure.
Directory Navigation as Systemic Cartography
Directories in Perl are not merely containers of files; they constitute a cartography of system organization. Reading directory contents, testing file attributes, and orchestrating directory creation or deletion are acts that extend Perl’s influence from the textual into the infrastructural. Each directory operation requires cognizance of platform-specific idiosyncrasies, error propagation, and permission hierarchies. Mastery of these techniques equips developers to implement automation that transcends single-machine constraints, enabling scripts to traverse heterogeneous environments with seamless adaptability.
Hashes and Arrays as Data Constellations
At the heart of Perl’s data management lies the manipulation of arrays and hashes, instruments for structuring information with elegant precision. Arrays allow sequential orchestration of elements, while hashes provide associative mapping that captures relationships and metadata with unparalleled efficiency. Nested combinations—arrays of hashes or hashes of arrays—form constellations of data capable of representing multi-dimensional realities, from user transaction histories to network topologies. When intertwined with file operations, these constructs permit the extraction of records, aggregation of statistics, and generation of tailored reports, transforming textual detritus into structured, insightful vistas.
Error Handling as Ritualized Safeguard
The discipline of error handling in Perl transcends mere precaution; it constitutes a ritualized safeguard, instilling resilience into scripts. Evaluating return values, judiciously invoking die statements, and providing descriptive diagnostic messages are practices that anticipate failure modes rather than merely reacting to them. In complex automation scenarios, these techniques prevent cascading faults, safeguard data integrity, and enhance maintainability. The emphasis on graceful degradation is emblematic of the CIW 1D0-437 ethos, reflecting an understanding that robust programming anticipates adversity and mitigates it through careful design.
Synthesis of Pattern, File, and Data
The confluence of pattern matching, file manipulation, and data structuring epitomizes Perl’s holistic utility. A script can traverse labyrinthine logs, isolate salient patterns using regular expressions of intricate sophistication, and channel extracted data into meticulously organized arrays or hashes. Subsequent operations may produce synthesized summaries, filtered reports, or alert mechanisms, each step building upon the prior in an orchestrated cascade of computational logic. This integration transforms Perl from a mere scripting language into a medium for data alchemy, where textual chaos is transmuted into comprehensible and actionable knowledge.
The Semantics of Persistent Storage
Persistent storage in Perl is not merely about retaining information; it is about encoding meaning within enduring structures. Files and directories serve as repositories not only of data but of context, provenance, and state. Scripts that interact with these artifacts must respect temporal coherence, handle concurrent access with discretion, and preserve semantic relationships inherent in the datasets. The sophisticated developer contemplates not only the immediate manipulation of bytes but the long-term implications of storage strategies, ensuring that each interaction leaves the digital landscape enriched rather than diminished.
Interfacing with External Data Ecosystems
Modern Perl applications rarely exist in isolation. Interfacing with external datasets—whether CSV files, JSON feeds, or relational repositories—demands a fluency in both format-specific conventions and the generalized paradigms of file handling. Parsing, validation, and normalization are essential, allowing heterogeneous sources to be assimilated into coherent internal structures. This interoperability transforms scripts into adaptive agents capable of bridging disparate systems, reflecting the real-world demands anticipated by CIW 1D0-437 exam objectives.
Temporal Analysis and Log Archaeology
Perl’s file handling capabilities enable temporal analysis and the excavation of informational strata within log archives. Scripts can sift through chronological records, identify anomalies, and reconstruct sequences of events with precision akin to digital archaeology. By combining pattern matching with temporal sorting and data aggregation, practitioners can uncover insights buried within voluminous datasets, transforming passive storage into a dynamic resource for decision-making, monitoring, and forensic investigation.
Perl’s Nexus with Data Repositories
Perl’s prowess manifests profoundly when navigating labyrinthine data repositories. By orchestrating interactions with relational databases, scripts transcend static execution, transmuting into dynamic agents capable of perspicaciously manipulating records. DBI, Perl’s quintessential conduit to databases, permits interlocution with myriad systems, rendering queries not merely as commands but as instruments of intricate data choreography. Developers, particularly aspirants of CIW 1D0-437, harness these abilities to construct applications where data persistence is paramount, user credentials are authenticated, and content is malleably managed. The intricate interweaving of connection strings, authentication schemas, and driver specifications transforms routine database operations into a sophisticated ballet of computational dexterity.
Scripting Queries with Elegance
Executing SQL within Perl transcends mere syntactic fidelity; it becomes an art of precise orchestration. Queries, whether for creation, retrieval, updating, or deletion of records, flow seamlessly into Perl’s arrays and hashes, enabling immediate algorithmic manipulation or aesthetic web presentation. This fluidity fosters an environment where the programmer’s intent is faithfully mirrored in both backend logic and frontend manifestation. Perl’s interpretive elasticity allows developers to marshal query results into structures that support complex computations, conditional rendering, and responsive interactions, thereby elevating mundane database operations into a realm of programmable elegance.
Fortifying Scripts Against Failure
Robustness is a hallmark of Perl’s database engagement. Erroneous connections or malformed queries need not precipitate catastrophic failure; Perl’s error handling mechanisms intercede with meticulous precision. The detection of anomalies, combined with graceful recovery routines, ensures scripts persist in a state of operational equilibrium. CIW 1D0-437 practitioners are encouraged to internalize these paradigms, cultivating resilience that mirrors industrial best practices. Through vigilant exception management and proactive logging, applications metamorphose into fortresses of stability, impervious to transient data aberrations or procedural inconsistencies.
Bridging the Web and Backend
Perl’s aptitude extends beyond data repositories, forging a seamless bridge between backend logic and interactive web interfaces. Modules such as CGI endow developers with the capacity to apprehend HTTP requests, decipher form submissions, and dynamically generate HTML responses. This interplay fosters immersive user experiences, where content is not merely delivered but orchestrated in real time according to user behavior. The integration of database interaction with web scripting transmutes static pages into responsive ecosystems, facilitating applications from rudimentary guestbooks to sophisticated content management systems with nuanced interactivity.
Safeguarding Against Digital Intrusions
In the crucible of web development, security emerges as an indispensable tenet. Input validation becomes a vigilant sentinel, ensuring data conforms to expected paradigms before it traverses the database or manifests on the user interface. Parameterized queries, sanitized inputs, and meticulous handling of session data collectively constitute a bulwark against pernicious exploits such as SQL injection or cross-site scripting. Aspiring CIW 1D0-437 candidates internalize these strategies, producing scripts that are not only functional but fortified against the vicissitudes of malicious interference. In this milieu, security is not ancillary but symbiotic with functionality, an intrinsic component of exemplary web design.
Experiential Learning Through Application
Pedagogical profundity is amplified through praxis. Constructing applications that interlace database connectivity with dynamic web generation provides learners with tangible fluency. Whether crafting a simple guestbook or an embryonic content management system, candidates navigate the intricacies of script-to-database communication, form input processing, and real-time response rendering. Each exercise consolidates conceptual understanding, fostering a synthesis of theory and practice that engenders both confidence and competence. This experiential immersion underscores Perl’s versatility, demonstrating its capacity to underpin professional-grade web solutions while nurturing the skills essential for certification and career advancement.
Harmonizing Performance and Scalability
The sophistication of database-driven applications is amplified by considerations of performance and scalability. Perl scripts, when judiciously architected, minimize latency in query execution and optimize resource utilization. Techniques such as connection pooling, query caching, and deferred data processing ensure applications respond nimbly to fluctuating user loads. High-engagement applications, particularly those that aggregate real-time data or service concurrent users, benefit from such optimizations. CIW 1D0-437 aspirants gain exposure to these strategies, appreciating the delicate balance between computational efficiency and architectural elegance required for professional-grade deployment.
Integrating Advanced Web Features
The modern web ecosystem demands more than static data rendering. Perl empowers developers to integrate sophisticated features such as asynchronous updates, dynamic content filtering, and interactive dashboards. By leveraging the synergy between CGI scripting, JavaScript augmentation, and database queries, developers orchestrate applications that anticipate and adapt to user behavior. This integration of technologies transforms conventional pages into interactive portals, where the backend responds to nuanced inputs in real time, cultivating a user experience imbued with immediacy and relevance. Mastery of these techniques situates candidates at the vanguard of contemporary web development paradigms.
Advanced Concepts in Perl Programming
Perl, often hailed as the Swiss Army knife of scripting languages, unveils a labyrinthine tapestry of constructs that transcend rudimentary coding. Learners embarking on the CIW 1D0-437 certification journey encounter paradigms that require cerebral agility, ranging from references and object-oriented design to nuanced modularization strategies. These advanced concepts are not mere embellishments; they are essential instruments for architecting scripts that are both resilient and scalable. Mastery in this domain signifies an elevation from transient scripting to professional-grade code craftsmanship, blending precision with expressive ingenuity.
The Elegance of References
In Perl, references constitute a cerebral pivot point for manipulating data structures with dexterity and finesse. By allowing the creation of nested arrays and hashes, references facilitate the orchestration of complex hierarchies without sacrificing clarity. Their utility extends to the efficient transmission of data to subroutines, where memory footprint and execution velocity become paramount. The judicious use of anonymous arrays and hashes amplifies this capability, enabling the design of architectures that can elegantly accommodate evolving datasets. Such techniques are not only emblematic of Perl’s expressive depth but are also recurrently emphasized in CIW certification scenarios, reinforcing the necessity of conceptual mastery.
Object-Oriented Programming Paradigms
Perl’s approach to object-oriented programming, though idiosyncratic, affords remarkable versatility for constructing maintainable and modular applications. Through encapsulation, developers can safeguard the integrity of data, while inheritance facilitates the creation of hierarchical structures that promote code reuse. Method invocation in Perl, with its syntactic subtlety, encourages the development of scripts that are both nimble and robust. Certification candidates must internalize these constructs, understanding the interplay between classes, objects, and polymorphic behavior. Beyond exam preparation, proficiency in OOP transforms Perl from a procedural workhorse into a formidable instrument for complex application development.
Modularization and Reusability
A cornerstone of advanced Perl programming lies in modularization, which enables developers to segment code into discrete, reusable components. This philosophy fosters maintainability, diminishes redundancy, and enhances collaborative potential in team environments. Modules encapsulate functionality, allowing scripts to leverage pre-existing libraries while retaining clarity. Best practices dictate adherence to consistent naming conventions, intuitive subroutine organization, and thorough commenting. These methodologies not only fortify code reliability but also cultivate a mindset aligned with professional software development standards.
Debugging and Error Management
Effective debugging transcends mere syntax correction; it embodies a meticulous examination of logic, data flow, and runtime behavior. Perl’s suite of diagnostic tools—including warnings, exception handling, and logging mechanisms—provides candidates with the arsenal necessary to preempt and resolve anomalies. Developing an analytical approach to error management fosters resilience and confidence, ensuring scripts perform reliably across diverse scenarios. CIW aspirants benefit from iterative exercises that simulate real-world debugging, solidifying their proficiency while reinforcing foundational concepts.
Strategies for Exam Readiness
Preparation for the CIW 1D0-437 examination necessitates a dual approach of conceptual comprehension and applied practice. Candidates must internalize objectives encompassing pattern matching, file operations, database interactions, and web integration. Practical exercises, such as constructing nested data structures or implementing object-oriented modules, solidify theoretical understanding. Simulated assessments hone time management and problem-solving acuity, enabling learners to navigate complex questions with poise. Acclimatization to Perl idioms—subtle syntactic and semantic nuances—further distinguishes adept candidates, equipping them to tackle questions that probe both technical proficiency and analytical dexterity.
Cultivating a Holistic Perl Mindset
Achieving fluency in Perl, particularly within the ambit of CIW 1D0-437 certification, extends beyond memorization. It demands a mindset of curiosity, experimentation, and iterative refinement. Each construct—whether a reference, object, or module—serves as a building block in a larger edifice of computational creativity. By engaging in deliberate practice, embracing best practices, and continually challenging one’s understanding, learners cultivate a dexterous command of the language. The journey is as much about cognitive enrichment as it is about credential attainment, embedding skills that endure across varied contexts of web development and automation.
Advanced Data Structures and Hierarchical Design
Perl’s capacity to construct multifaceted data structures lies at the heart of its enduring appeal among seasoned developers. Beyond elementary arrays and hashes, Perl permits the crafting of nested, hierarchical configurations that elegantly mirror complex real-world datasets. These structures, when orchestrated via references, empower programmers to traverse and manipulate information with a sophistication rarely encountered in simpler scripting languages. Conceptualizing data in layered arrangements enhances analytical clarity, ensuring that algorithms are both efficient and intelligible. For candidates preparing for CIW 1D0-437, the ability to seamlessly implement such architectures demonstrates an aptitude for handling advanced programming scenarios with aplomb.
Anonymous Structures and Memory Efficiency
Anonymous arrays and hashes represent a subtle yet potent instrument within Perl’s repertoire. These structures, devoid of explicit identifiers, offer ephemeral storage mechanisms that reduce namespace clutter and bolster memory efficiency. They are particularly advantageous when constructing temporary datasets for iterative processing or when passing complex data to subroutines. The ephemeral nature of these constructs necessitates meticulous understanding, as improper usage can precipitate unintended memory retention or convoluted debugging scenarios. Mastery of anonymous structures not only elevates script elegance but also aligns with professional standards, reinforcing sustainable programming practices.
Mastering Pattern Matching and Regular Expressions
Pattern matching, executed through Perl’s extensive regular expression framework, constitutes a cornerstone of data parsing and transformation. This capability transcends simple text searches, enabling developers to execute intricate queries, validate input, and extract multifarious patterns from voluminous datasets. Regular expressions, when wielded with precision, transform Perl scripts into instruments of extraordinary analytical power. Certification aspirants must grasp both the syntax and strategic application of these constructs, recognizing subtleties such as greedy versus non-greedy quantifiers, lookahead assertions, and backreferences. The ability to synthesize complex patterns with efficiency epitomizes advanced Perl proficiency.
Object-Oriented Elegance and Methodical Abstraction
The abstraction afforded by object-oriented Perl extends beyond conventional encapsulation. By leveraging inheritance and polymorphism, developers can construct hierarchies that reflect intricate domain models, promoting both modularity and scalability. Methodical design ensures that responsibilities are judiciously allocated among classes, reducing coupling while enhancing cohesion. In professional contexts, this enables scripts to evolve gracefully alongside expanding requirements, mitigating technical debt. For CIW candidates, a profound understanding of object-oriented abstraction is indispensable, as exam scenarios frequently probe the capacity to architect maintainable, adaptable solutions.
Modular Design Patterns and Reusable Components
Perl modules represent more than mere convenience; they embody a philosophy of code economy and intelligibility. Through modular design patterns, developers can isolate discrete functionality, facilitating both reuse and collaborative development. Modules encourage consistent interfaces, allowing disparate components to interact seamlessly while preserving autonomy. In advanced Perl practice, attention to naming conventions, subroutine clarity, and dependency management becomes critical, as these elements collectively determine the maintainability of elaborate applications. For certification preparation, the disciplined construction and utilization of modules signify a readiness to tackle both theoretical and practical challenges.
Debugging Paradigms and Analytical Problem-Solving
Advanced Perl mastery necessitates a methodical approach to debugging, integrating both automated tools and cognitive rigor. Warnings and error messages serve as navigational aids through the labyrinth of potential pitfalls, while logging mechanisms provide longitudinal insights into script execution. Candidates must cultivate a mindset of analytical discernment, tracing logic pathways and anticipating emergent behaviors within code. The practice of hypothesizing, testing, and iteratively refining solutions transforms debugging from a reactive chore into a proactive strategy, reinforcing both technical acumen and creative problem-solving skills. Such expertise is directly relevant to CIW assessments, which often evaluate both conceptual comprehension and practical execution.
File Handling and Persistent Data Management
The manipulation of files, encompassing reading, writing, and structured storage, constitutes a domain of perennial importance within Perl development. Advanced practitioners employ nuanced strategies for streamlining I/O operations, ensuring data integrity while optimizing performance. Techniques such as buffered reading, selective parsing, and atomic file writes exemplify the sophisticated approaches demanded in professional contexts. Candidates preparing for CIW 1D0-437 must internalize both the syntactic and procedural aspects of file management, recognizing that efficiency, accuracy, and error handling are equally paramount. Mastery in this arena enables scripts to interface seamlessly with external datasets, databases, and web resources, enhancing overall functionality.
Database Interaction and Dynamic Integration
Perl’s versatility extends naturally into database interactions, where the ability to query, manipulate, and persist data defines a script’s operational efficacy. Advanced practitioners utilize modules such as DBI to establish connections, execute parameterized queries, and manage transactional integrity. This interaction demands not only technical proficiency but also a strategic understanding of schema design, query optimization, and error recovery. For certification candidates, the capacity to integrate dynamic data sources with clarity and precision represents a pivotal competency, reflecting both pragmatic skill and theoretical insight.
Web Integration and Scripting Synergy
In the contemporary digital ecosystem, Perl’s aptitude for web integration remains a vital asset. Scripts can interface with HTTP protocols, manipulate form submissions, parse markup languages, and automate content retrieval with fluidity. The orchestration of these capabilities requires a synthesis of multiple advanced concepts—references, regular expressions, modularization, and object-oriented design—culminating in scripts that are both resilient and adaptive. CIW candidates benefit from immersive exercises in web interaction, as these scenarios mirror practical challenges encountered in professional development, ensuring that theoretical knowledge is effectively translated into executable competence.
Best Practices for Maintainable Code
Sustained success in Perl programming hinges upon adherence to established best practices, which encompass clarity, consistency, and conscientious documentation. Consistent naming conventions foster readability, while modular design and clear subroutine delineation enhance both maintainability and scalability. Comprehensive commentary elucidates complex logic, serving as a cognitive bridge for future developers or collaborators. By internalizing these principles, candidates cultivate scripts that transcend mere functionality, embodying craftsmanship and foresight. This discipline not only facilitates exam preparedness but also instills a mindset aligned with enduring professional excellence.
Orchestrating Complex Database Transactions
Perl’s versatility shines luminously when orchestrating multifaceted database transactions. Beyond rudimentary CRUD operations, the capacity to execute nested transactions, commit or rollback operations, and ensure atomicity transforms scripts into potent instruments of data integrity. Developers engaged in CIW 1D0-437 training encounter scenarios requiring transactional acumen, where a single misstep can propagate inconsistencies. By leveraging Perl’s transaction-handling capabilities, scripts can maintain coherence across interconnected tables, synchronize operations between diverse databases, and enforce business logic that mirrors real-world constraints. This meticulous orchestration imbues applications with a sense of reliability that transcends basic functionality, cultivating an ecosystem of trust and precision.
Dynamic Form Handling and User Interaction
User interaction is the lifeblood of modern web applications, and Perl excels in capturing, processing, and responding to dynamic inputs. Through CGI scripting, forms evolve from static receptacles into interactive conduits, channeling user data seamlessly into backend processes. Each input field becomes an opportunity to validate, sanitize, and contextualize information before committing it to the database. Advanced techniques, such as conditional rendering, adaptive validation, and context-aware prompts, empower developers to create responsive experiences that anticipate user needs. CIW 1D0-437 candidates benefit from mastering these mechanisms, learning to convert abstract form submissions into structured, actionable data flows that fuel dynamic web environments.
Real-Time Data Rendering and Manipulation
The fusion of Perl and database interaction unlocks unprecedented potential for real-time data rendering. Rather than relying on static snapshots, scripts can query live datasets and render responses with immediacy, reflecting the current state of the underlying system. Arrays, hashes, and nested structures facilitate rapid transformations, enabling sophisticated filtering, sorting, and aggregation operations before presentation. This capability is particularly vital in applications such as live dashboards, inventory management systems, and interactive analytics tools. By internalizing these techniques, developers acquire the aptitude to produce interfaces that are not only functional but dynamically responsive, cultivating heightened user engagement and operational transparency.
Advanced Error Handling and Resilience Strategies
Perl’s architecture encourages a proactive approach to error management, extending beyond simple exception catching. Sophisticated strategies involve anticipating potential failure points, constructing contingency routines, and implementing layered logging mechanisms that capture context-rich diagnostic information. In CIW 1D0-437 scenarios, this translates into scripts that can gracefully recover from network interruptions, invalid queries, or unforeseen user input without compromising data integrity or user experience. This culture of anticipatory resilience fosters confidence among developers, transforming error handling from a reactive necessity into a strategic advantage that enhances system reliability and professional credibility.
Modular Design and Reusability
The elegance of Perl lies not only in its functionality but in its capacity for modularity and code reuse. By encapsulating database interaction, form processing, and HTML generation into discrete modules, developers can construct maintainable, extensible, and coherent architectures. This modular approach minimizes redundancy, enhances clarity, and accelerates development cycles. CIW 1D0-437 aspirants are encouraged to adopt these paradigms, cultivating a coding discipline that mirrors industry expectations. Modules can be tailored for specific purposes, shared across multiple projects, or adapted to evolving requirements, thereby reinforcing a culture of efficiency and adaptability in professional web development contexts.
Security-First Mindset in Web Applications
A security-first mindset is indispensable when interfacing with databases and web platforms. Perl equips developers with tools to implement multifaceted security measures, including parameterized queries, input validation, encryption, and secure session management. Beyond these, awareness of emerging vulnerabilities, such as cross-site request forgery or injection attacks via unconventional channels, ensures that applications remain robust in hostile environments. CIW 1D0-437 training emphasizes this proactive vigilance, cultivating developers who internalize security as an inseparable component of functional design. This mindset promotes trust, compliance, and resilience in applications deployed within complex digital ecosystems.
Leveraging APIs for Enhanced Functionality
The modern web thrives on interoperability, and Perl provides avenues to integrate with diverse APIs for augmented functionality. RESTful endpoints, SOAP services, and custom web services can be seamlessly accessed to enrich applications with external data or functionality. For instance, integrating third-party authentication, mapping services, or analytics engines allows applications to transcend isolated operation, creating richer, more interconnected user experiences. Mastery of API integration equips CIW 1D0-437 candidates with a versatile skill set, enabling them to craft applications that interact fluidly with broader digital landscapes while maintaining coherence and reliability.
Performance Optimization and Scalability Considerations
Efficiency and scalability are cornerstones of professional-grade web applications. Perl’s flexibility allows developers to fine-tune queries, cache recurrent data, and implement asynchronous processing to mitigate latency and maximize throughput. Understanding the nuances of indexing, query optimization, and resource management empowers developers to handle escalating user demands without degradation in performance. CIW 1D0-437 aspirants benefit from exposure to these techniques, gaining insights into the balance between rapid responsiveness and sustainable resource utilization. Applications crafted with this attention to performance exhibit both robustness under load and elegance in execution.
Sophisticated Logging and Auditing Mechanisms
Maintaining visibility into database and web application operations is pivotal for both debugging and compliance. Perl enables the construction of sophisticated logging and auditing mechanisms that record granular activity, trace execution paths, and capture contextual metadata. Such systems allow developers to detect anomalies, monitor usage patterns, and validate operational integrity with precision. For CIW 1D0-437 candidates, the cultivation of these practices reinforces both technical acumen and professional accountability, ensuring that applications are transparent, traceable, and aligned with regulatory or organizational standards.
Integrating Multimodal Data Sources
Modern applications often require the amalgamation of diverse data sources, ranging from structured relational databases to semi-structured JSON feeds or unstructured textual repositories. Perl’s parsing capabilities, combined with robust database connectivity, facilitate the seamless integration of these multimodal sources. Scripts can normalize disparate datasets, reconcile schema variations, and synthesize actionable insights in real time. CIW 1D0-437 practitioners develop proficiency in these techniques, equipping them to handle complex data ecosystems where information heterogeneity is the norm rather than the exception.
Real-World Project Simulations
Hands-on project simulations provide an immersive avenue to consolidate theoretical knowledge. By constructing multi-component applications that incorporate database interaction, web integration, security, and performance considerations, candidates experience the holistic challenges of professional web development. These simulations encourage experimentation, iterative refinement, and troubleshooting in controlled scenarios, cultivating a mindset attuned to both innovation and precision. Such experiential learning reinforces conceptual understanding while engendering the confidence to deploy Perl-based solutions in real-world contexts.
Event-Driven Architecture in Perl
Event-driven architecture, often associated with responsiveness and asynchronous processing, can be effectively implemented using Perl. Scripts can respond to triggers such as database updates, user actions, or system events, initiating predefined routines or cascading workflows. This paradigm enhances interactivity, minimizes latency, and allows applications to adapt dynamically to environmental conditions. For CIW 1D0-437 aspirants, understanding event-driven design promotes a nuanced approach to responsive development, where user experiences are anticipatory rather than reactive, and backend processes operate with coordinated precision.
Custom Reporting and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is contingent upon the ability to generate insightful reports and perform nuanced analytics. Perl’s capabilities extend into the generation of customized reports, dynamic charts, and data summaries derived directly from underlying databases. By automating report generation, filtering results based on user-defined parameters, and integrating visualizations, developers can transform raw data into actionable intelligence. CIW 1D0-437 candidates gain practical exposure to these methodologies, reinforcing the connection between technical implementation and strategic insight within web-based systems.
Scripting Dynamic Data Pipelines
Perl excels in orchestrating dynamic data pipelines, where information flows from disparate sources through multiple transformative stages. Such pipelines often involve reading unstructured files, filtering content through complex regular expressions, mapping data into arrays or hashes, and finally exporting structured summaries for downstream consumption. The elegance of Perl lies in its capacity to handle each stage with minimal verbosity while maintaining maximal clarity. Developers may intersperse error checks, validation routines, and logging mechanisms, ensuring that even the most intricate pipeline maintains coherence and reliability. In production contexts, this capability allows administrators to automate end-to-end workflows that would otherwise demand laborious manual intervention.
Lexical Precision in File Parsing
Parsing files in Perl is an exercise in lexical precision, where every character, delimiter, and whitespace carries semantic weight. Unlike superficial tokenization, high-level parsing often entails context-aware extraction, pattern-based substitutions, and conditional accumulation of records. For instance, a server log may contain multiline entries, irregular timestamps, and embedded metadata, requiring scripts to employ both lookahead and lookbehind assertions in regular expressions to capture relevant fragments. This meticulous approach ensures that extracted data retains fidelity to its source, enabling subsequent processing to operate on accurate, contextually coherent information rather than crude approximations.
The Cartography of Nested Data Structures
Nested data structures in Perl—hashes of arrays, arrays of hashes, and beyond—constitute a form of digital cartography. Each layer represents a dimension of meaning, from hierarchical configurations to associative mappings of identifiers to attributes. Constructing these structures demands strategic planning: one must balance memory efficiency, accessibility, and the mutability of elements. When paired with file operations, these structures facilitate sophisticated data aggregation, filtering, and reporting mechanisms. A script can, for example, read multiple CSV files, organize records by region and timestamp, and output synthesized summaries that reveal both granular and macro-level trends.
Persistent Metadata and Attribute Management
Beyond content storage, Perl allows scripts to interrogate and manipulate file metadata—permissions, timestamps, ownership, and type. This attribute management is crucial for scripts that operate in shared environments, where improper handling can lead to unauthorized access, inadvertent overwrites, or systemic failures. Incorporating metadata checks into file operations transforms routine tasks into disciplined procedures, ensuring that automation respects the integrity of the underlying filesystem. The CIW 1D0-437 examination emphasizes such practices, requiring candidates to demonstrate proficiency not only in file content manipulation but also in comprehensive environmental awareness.
Streamlined Error Propagation
Error handling in Perl transcends localized exception trapping; advanced practitioners implement streamlined propagation mechanisms that cascade failures in a controlled, informative manner. By leveraging return-value evaluation, die statements with contextually rich messages, and eval blocks, scripts can manage both expected and unforeseen anomalies. This orchestration transforms Perl code from fragile sequences of operations into resilient frameworks capable of self-diagnosis, reporting, and mitigation. The result is automation that behaves predictably even under volatile conditions, preserving both data integrity and operational continuity.
Transformative Regular Expressions
Regular expressions in Perl are not mere pattern-matching instruments; they are transformative tools that convert textual chaos into structured knowledge. With features such as non-greedy quantifiers, capture groups, and conditional assertions, regex can extract embedded metadata, normalize inconsistent formats, and even validate complex syntactic constructs. When applied to file content, this capability enables scripts to identify anomalies, segment multi-part entries, or replace archaic terminology with standardized equivalents. The interplay of regex and file I/O epitomizes Perl’s philosophy: elegant conciseness married to functional potency.
Temporal Orchestration and Log Chronology
Manipulating temporal data in logs involves both sorting and contextualization. Perl scripts can interpret timestamps in various formats, align entries chronologically, and detect sequential anomalies indicative of system malfunctions or security events. By storing intermediate results in structured arrays or hashes, developers can perform temporal aggregations, identify recurring patterns, and generate alerts based on deviations from expected behavior. This temporal orchestration is vital for system administrators and developers alike, offering insights that transcend simple content inspection and venture into predictive analytics.
Automated Archival and Cleanup
File management in Perl extends into automated archival and cleanup routines, essential for sustaining system hygiene. Scripts can detect aged or redundant files, compress content for long-term storage, or migrate data across directories according to predefined policies. Coupled with logging and reporting mechanisms, these routines provide transparency and traceability, ensuring that automated housekeeping does not compromise operational awareness. The sophistication lies in balancing automation with prudence: every deletion or relocation must be reversible or at least auditable to prevent inadvertent data loss.
Integrating External Data Formats
Perl’s versatility shines in integrating diverse data formats. CSV, TSV, JSON, XML, and proprietary log formats can all be parsed, transformed, and reconstituted into standardized internal structures. The challenge often lies not in basic parsing but in reconciling inconsistencies—varying delimiters, embedded special characters, or incomplete records. Advanced scripts implement validation layers, corrective substitutions, and normalization procedures, producing datasets that are both accurate and structurally coherent. This ability to harmonize disparate sources underpins many real-world automation workflows, from analytics pipelines to monitoring frameworks.
Data Filtration and Conditional Aggregation
Data filtration in Perl involves selectively retaining records based on complex criteria, often spanning multiple fields and conditions. Hashes serve as natural indices for quick lookup, while arrays allow sequential accumulation and sorting. Conditional aggregation enables scripts to compute statistics, detect anomalies, or generate customized summaries without extraneous overhead. For instance, a script processing sales logs might filter transactions by region, aggregate totals by product category, and output alerts for abnormal patterns. This paradigm illustrates how Perl enables both precision and scalability in data management tasks.
The Semiology of Logs
Logs are more than repositories of events; they are semiotic artifacts, encoding system behavior, user interactions, and operational anomalies. Perl scripts function as interpretive tools, translating these semiotic signals into actionable insights. By combining regex extraction, temporal ordering, and structured storage, scripts can identify subtle patterns indicative of recurring faults, security intrusions, or performance bottlenecks. This interpretive approach elevates file handling from mechanical operations to analytical craftsmanship, embodying the synergy of technical proficiency and cognitive acuity required for high-stakes environments.
Recursive Traversal and Hierarchical Analysis
Recursive directory traversal is a sophisticated technique enabling scripts to explore nested hierarchies, identify relevant files, and perform batch operations. Coupled with conditional logic, scripts can selectively process files based on type, size, timestamp, or content patterns. This hierarchical analysis is invaluable for system audits, bulk configuration updates, and archival tasks. The methodology mirrors principles of digital archaeology: uncovering nested structures, cataloging artifacts, and synthesizing coherent representations of complex information landscapes.
Conditional File Locking and Concurrency
Concurrent access to files introduces potential conflicts and race conditions. Perl accommodates conditional file locking mechanisms that serialize access, ensuring data integrity in multi-user or multi-process environments. Properly implemented locks prevent data corruption while maintaining throughput, an essential consideration in enterprise contexts where scripts may operate on shared resources. Understanding these concurrency paradigms reflects a mature grasp of both operational and theoretical aspects of file management.
Real-Time Monitoring and Reactive Automation
Perl’s file handling capabilities support real-time monitoring, where scripts react dynamically to changes in the filesystem. By periodically polling files or employing notification mechanisms, automation scripts can detect modifications, trigger processing pipelines, and generate alerts with minimal latency. This reactive paradigm transforms static scripts into interactive agents capable of continuous oversight, turning mundane file operations into proactive system management.
Modular File Handling for Maintainability
Advanced Perl development emphasizes modularity, encapsulating file handling routines within reusable subroutines or modules. This approach enhances maintainability, reduces redundancy, and facilitates testing. For instance, a generic file reader may accept dynamic parameters for path, encoding, and processing callbacks, allowing it to serve multiple scripts with minimal modification. Such architectural discipline ensures that even intricate automation remains comprehensible, debuggable, and adaptable to evolving requirements.
Transforming Data into Intelligence
The ultimate objective of file handling and data management in Perl is the transformation of raw data into intelligence. By leveraging structured storage, temporal analysis, pattern extraction, and filtration, scripts convert static textual artifacts into dynamic knowledge representations. Whether generating operational summaries, identifying anomalous behavior, or supporting decision-making, the combination of these techniques epitomizes practical mastery. The CIW 1D0-437 framework encapsulates this philosophy, emphasizing that theoretical proficiency attains true value only when translated into actionable, efficient solutions.
Conclusion
Mastering Perl for the CIW 1D0-437 certification is more than memorizing syntax—it is about cultivating a mindset of flexibility, creativity, and problem-solving. Throughout this six-part journey, learners explore the full breadth of Perl’s capabilities, from basic variables and control structures to advanced concepts like regular expressions, file handling, database interaction, and object-oriented programming. Each topic builds upon the last, reinforcing not only technical knowledge but also practical application skills essential for web development and automation.
Perl’s unique philosophy of “There’s more than one way to do it” encourages experimentation and innovation, enabling developers to approach challenges with multiple solutions in mind. By understanding context-sensitive evaluation, leveraging modular code with subroutines, and utilizing powerful text-processing features, candidates can write scripts that are both elegant and efficient. This adaptability aligns perfectly with real-world demands, ensuring that skills gained for certification translate directly into professional competence.
Emphasizing best practices, such as modularity, error handling, security-conscious coding, and maintainability, ensures that learners produce reliable and professional-grade scripts. Practical exercises—ranging from simple text parsing to dynamic web integration with databases—reinforce understanding while providing hands-on experience. This combination of theory and practice positions candidates to succeed in the CIW 1D0-437 exam with confidence and precision.
Ultimately, mastering Perl is a journey of discovery, creativity, and technical growth. The CIW 1D0-437 certification serves as both a benchmark of proficiency and a stepping stone toward advanced web development and automation tasks. By embracing Perl’s versatility and exploring its diverse features with curiosity and diligence, learners not only achieve certification success but also unlock a powerful toolset that will enhance their programming capabilities for years to come.
Perl is more than a language—it is a gateway to innovation, efficiency, and mastery in the ever-evolving world of web development.